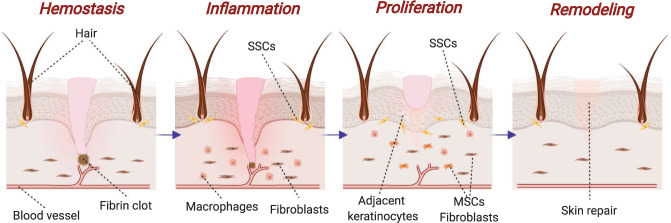
Fig. 1. Phases of skin wound healing process.
Hemostasis: activation of fibrin is responsible of clot formation and bleeding is stopped. Inflammation: damaged cells are phagocyted and factors are released to provoke cell migration and proliferation. Proliferation: cells such as dermal fibroblasts, MSCs and SSCs (mesenchymal and skin stem cells) achieve wound’s site and form a provisional extracellular matrix. Remodeling: collagen fibers are realigned, and residues are removed. Created with BioRender.com.