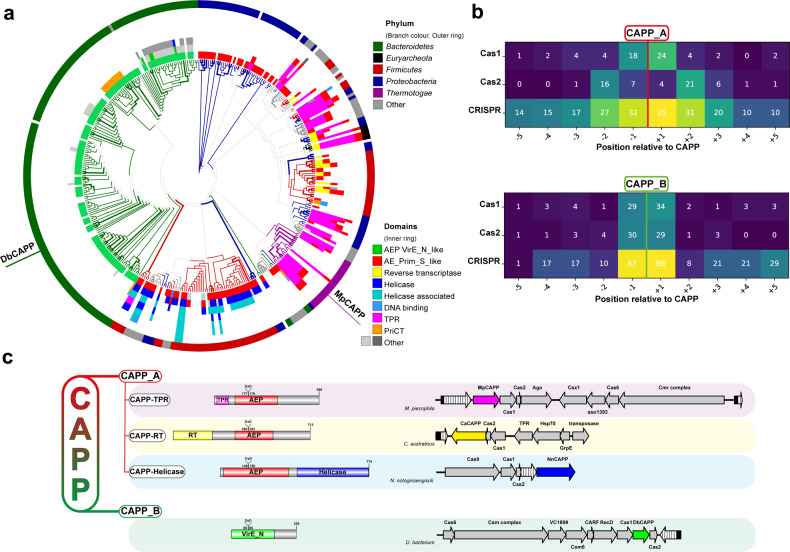
Fig. 1. Bioinformatic analysis of CRISPR-associated Prim-Pols.
a A phylogenetic tree (bootstrap n = 100) from multiple sequence alignments of all identified CAPP proteins (Supplementary Data 1 and 2). Branch colours and outer ring colours indicate phyla from the National Center for Biotechnology (NCBI) taxonomy database. The inner ring is composed of coloured protein domain annotations of CAPP proteins from the NCBI Conserved Domains Database (CDD; abbreviated terms are used to simplify colour coding, see Supplementary Fig. 1 for full description). Bootstrap values of 100% are indicated with bold branches. b Coloured heatmap of keywords from gene names, upstream and downstream of the CAPP genes, indicating their occurrence (%) at certain positions relative to CAPP. c Classification of CAPP proteins based on their sequence homology, forming two major classes CAPP_A and CAPP_B. CAPP_A is further divided to three types, based on the protein domain architectures, CAPP-TPR, CAPP-RT and CAPP-Helicase. For each class, an example of NCBI CDD derived domain architecture is shown (left), together with its corresponding operonic region (right) showing the neighbouring genes present in each operon. CRISPR repeat array – white textured arrow. TPR – tetratricopeptide repeat – magenta domain, RT – reverse transcriptase – yellow domain, VirE_N – virulent protein E N-terminal like – green domain, helicase - blue domain.