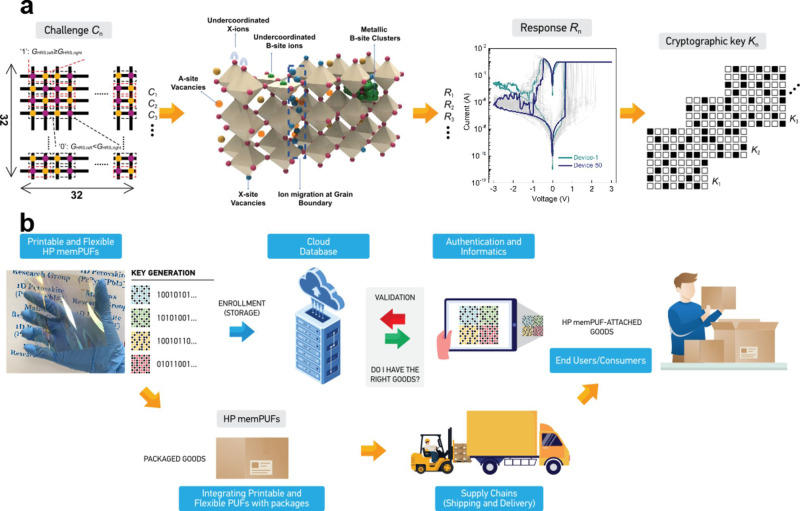
Fig. 1. Halide perovskite memristor PUFs (HP memPUFs).
a HPs possess a rich reservoir of intimately coupled charge transport properties that could serve as sources of entropy to design new kinds of PUFs. Examples include electrochemical metallization reactions, formation of metallic Pb clusters, vacancy-driven valence change mechanisms, ion migration, grain boundary effects, and so on. Here, stochasticity in the high resistance state of HP memPUF cells in the crossbar provides parametric support for the generation of unique cryptographic keys. Design flow: A differential readout strategy is adopted to read the resistance of the memory cells→ coexistence of a multitude of switching physics in halide perovskites enables high stochasticity of the resistance states→ the differences in the I–V curves of the memristor cells reflect this stochasticity→ cryptographic keys are generated from the difference in the high resistance state of these memristors. b Concept schematic of product authentication. The flexible HP memPUFs developed can be attached to the packaging of goods or products by the original manufacturer. Each individual product would have a unique PUF ID. End users (e.g., consumers or other entities along the supply chain) can validate the product and certify the provenance by accessing the enrolled keys in a secure cloud database. In addition, the HP memPUF array could be used to store other useful information such as product expiration date, supply chain path, etc relevant to the specific product.