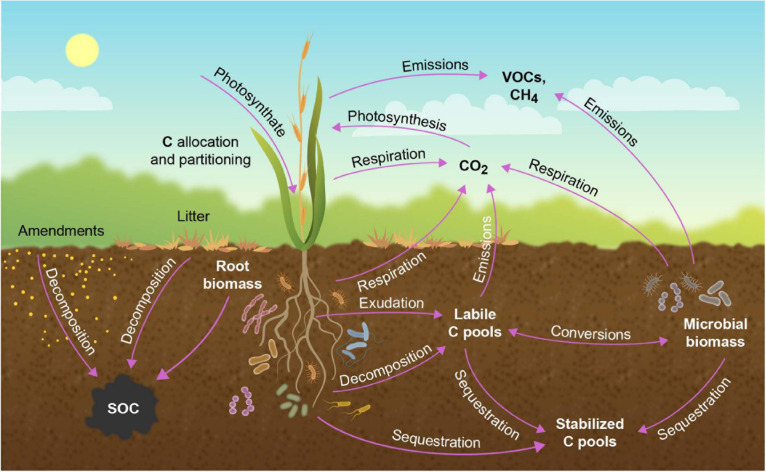
FIGURE 2.
Transfer of atmospheric CO2 into biotic and pedologic carbon (C) pools the plant ecosystem. Carbon enters the soil as root exudates or via decomposition of root or aboveground biomass. In the soil, C exists in root or microbial biomass, as bioavailable labile organic C, or as more recalcitrant C. Carbon exits the soil as direct emissions, or via root or microbial respiration, with microbial-mediated soil respiration being the major source of CO2 from terrestrial ecosystems. Carbon is also lost from the ecosystem as volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and methane (CH4). Modified from Jansson et al. (2018).