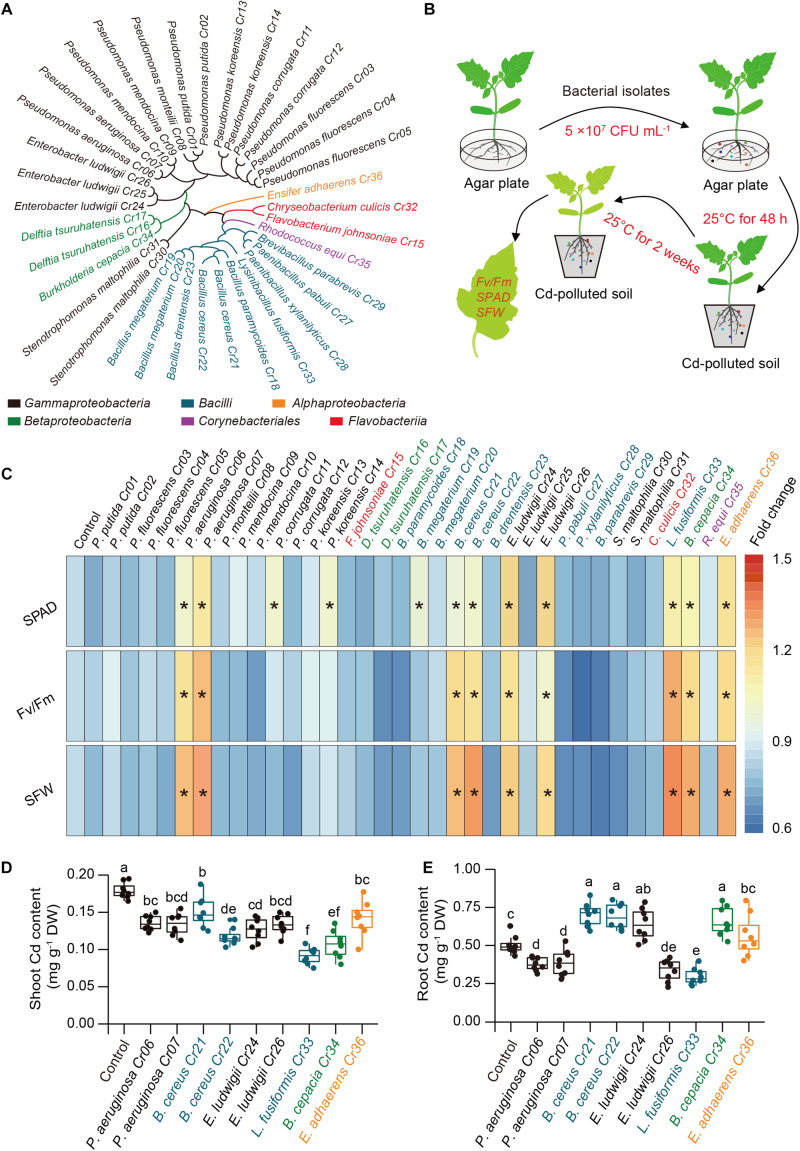
FIGURE 1.
Effects of soil drench with endophytic bacteria on Cd resistance in tomato plants. (A) Taxonomic cladogram of bacterial isolates. (B) High-throughput assays of Cd-detoxifying bacterial isolates. Ten-day-old tomato roots were co-cultured with or without bacterial suspension on agar plate at 25°C in the dark for 48 h. the non-inoculated (control) and inoculated plants were then transplanted into Cd-contaminated soils (100 mg Cd kg–1 soil) at 25°C. After 2 weeks of culture, the values of Fv/Fm, SPAD and SFW were determined for assessing the ability of plants to tolerate Cd stress. (C) Heatmap analysis for Fv/Fm, SPAD and SFW. Asterisks indicated significant differences between the control and inoculated plants (n = 8 biological replicates) using Student’s test at p < 0.05. (D) Shoot and (E) root Cd content. Different letters indicated significant differences among different bacterial strain-inoculated plants (n = 8 biological replicates) using Duncan’s multiple range test at p < 0.05.