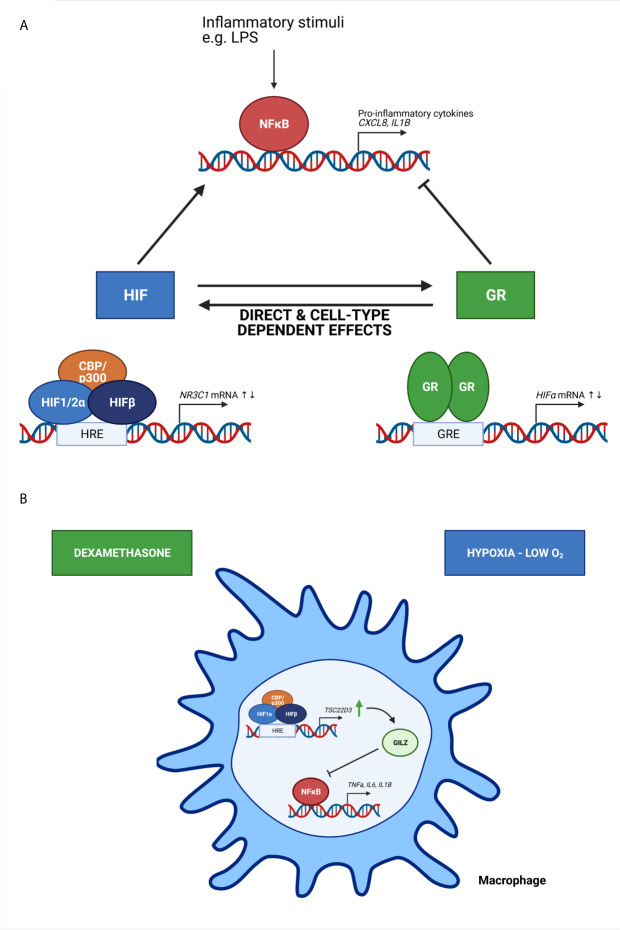
Figure 4.
The crosstalk between HIF and GR and its effect on NF-κB activity (A) and the effect of oxygen availability on immune cells (B). (A) Based on in vitro studies, HIF and GR have direct and cell-type dependent effects on each other, thereby increasing or repressing the transcription of HIF mRNA and N3RC1 mRNA genes. Inflammatory stimuli like lipopolysaccharide (LPS) induce NF-κB mediated transcription of genes encoding pro-inflammatory cytokines. HIF is known to stimulate this NF-κB mediated gene transcription, while GR will repress this. (B) Upon hypoxic conditions, the expression of GC-induced leucine zipper (GILZ) encoded by the TSC22D3 gene is upregulated, thereby inhibiting the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines mediated by NF-κB. When macrophages are pre-treated with dexamethasone, a synthetic GC, the effects are amplified. Figures created with Biorender.