Figure 1.
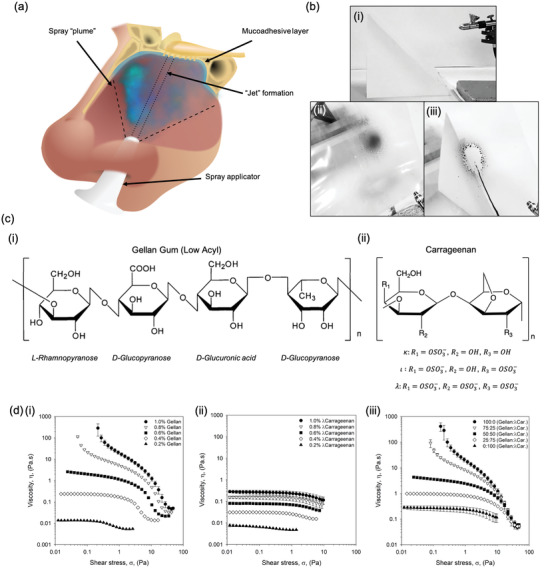
Defined nasal spray behaviors. a) Schematic diagram demonstrating the application of a nasal spray to the nasal cavity. b) Typical images obtained during screening of numerous mucoadhesive polymers for their ability to evenly spray and be retained on a 45° incline: i) spray set up, ii) gellan gum 1% (w/v) with black dye, and iii) alginate 1% (w/v) with black dye. c) Molecular structures of: i) gellan gum (low acyl), and; ii) carrageenan, where changes in the “R” groups provide variations for k, ι, and l. d) Dynamic viscosity profiles from high to low shear stress for: i) gellan samples with concentrations ranging from 0.2 to 1.0% (w/v), ii) l‐carrageenan samples with concentrations ranging from 0.2 to 1.0% (w/v), and iii) composite systems of gellan:l‐carrageenan at a total polymer concentration of 1% (w/v).
