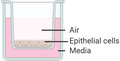
Table 3.
Most common in vitro respiratory models to study host–pathogen interactions
| Model type | Advantages | Disadvantages | In vitro example of host pathogen interaction | Cell type(s) used |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Submerged cell line culture
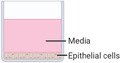
|
|
|
Respiratory syncytial virus[ 70 ] | Bronchial cell line (BEAS‐2B); Primary human nasal and bronchial epithelial cells. |
|
ALI monoculture
|
|
|
SARS‐CoV[ 72 ] | Primary human alveolar type II cells. |
| SARS‐CoV[ 92 ] | Calu‐3 cell line. | |||
ALI co‐culture
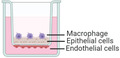
|
|
|
Aspergillus (A.) fumigatus [ 73 ] | Human primary bronchial epithelial cells, small airway cells, human blood derived macrophages, and dendritic cells. |
Polymer scaffolds

|
|
|
Influenza A[ 115 ] | Human primary small epithelial cells. |
| Papain (mimics air bourne allergen)[ 81 ] | Calu‐3 epithelial cell line, MRC‐5 fibroblast cell line, blood‐derived dendritic cells. | |||
Organoids

|
|
|
Parainfluenza[ 86 ] | Human embryonic stem cells. |
| Respiratory syncytial virus[ 85 ] | Human embryonic stem cells. | |||
| Multiple emerging influenza virus[ 91 ] | Tissue resident adult stem cells. | |||
|
Precision cut lung slices (PCLS)
|
|
|
Influenza[ 88 ] | Healthy lung slices from cancer patients undergoing lung resection. |
| Rhinovirus[ 89 ] | Healthy and asthmatic lung slices from patient donors. | |||
| LPS (mimics bacterial infection)[ 90 ] | Lung slices from patients with a variety of medical conditions from the National Disease Research Interchange. |
Cartoon insets created using BioRender.com.
This article is being made freely available through PubMed Central as part of the COVID-19 public health emergency response. It can be used for unrestricted research re-use and analysis in any form or by any means with acknowledgement of the original source, for the duration of the public health emergency.