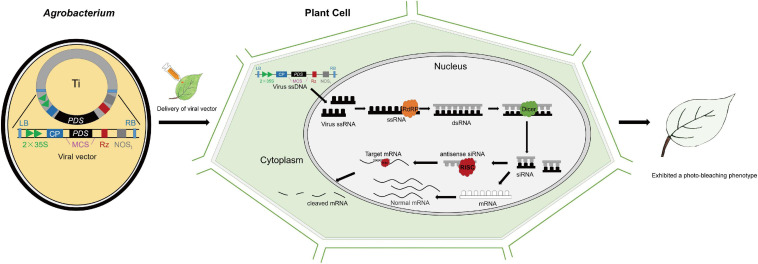
FIGURE 1.
Virus-induced gene silencing (VIGS) mechanism. Phytoene desaturase (PDS) serves as an example. Upon infection, the T-DNA carrying the viral genome is transformed into the plant by Agrobacterium and then transcribed by the host’s RNA polymerase. RNA-dependent RNA Polymerase (RdRP) (yellow) produces double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) from the single-stranded RNA (ssRNA) viral transcript. The dsRNA is then recognized by DICER-like enzyme, Dicer (green) and cleaved into short interfering RNAs (siRNAs). Antisense siRNAs are recognized by RNA-induced silencing complex, RISC (red) and melted into ssRNAs, which then serve as templates for target gene degradation. The single-stranded siRNAs are amplified and spread as mobile silencing signals throughout the plant, thus resulting in target gene silencing in plant organs distant from the site of infection, symbolized by the photo-bleaching phenotype of the entire leaf. LB: left border; RB: right border; 2 × 35S: duplicated cauliflower mosaic virus 35S promoter; CP: coat protein; MCS: multiple cloning site; PDS: PDS cDNA fragment; Rz: self-cleaving ribozyme; NOSt: nopaline synthase terminator.