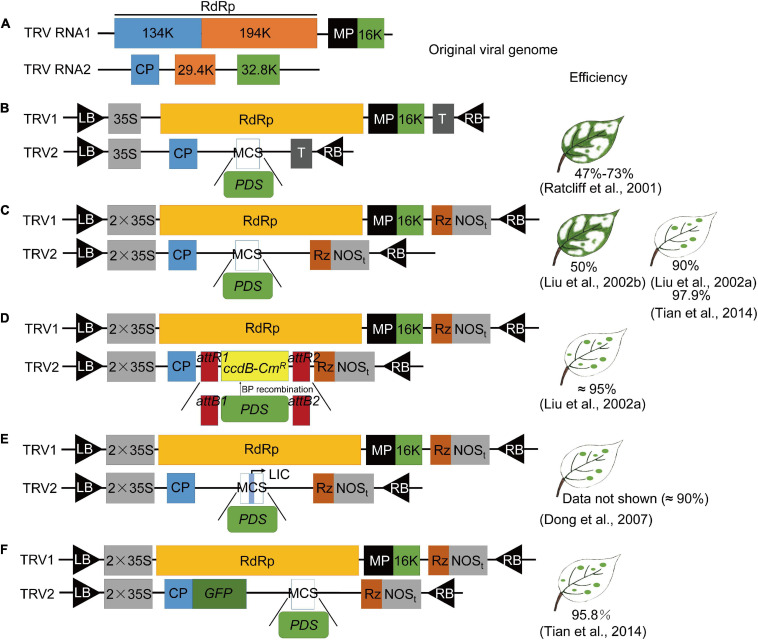
FIGURE 2.
The development process of TRV vector construction. Phytoene desaturase, PDS was used as an example. (A) Genome organization of tobacco rattle virus (TRV). The TRV1 open reading frames (ORFs) correspond to 134 and 194 kDa replicases, a movement protein (MP), and a 16 kDa cysteine-rich protein (16K). The TRV2 ORFs correspond to the coat protein (CP) and 29.4 and 32.8 kDa proteins (29.4K and 32.8K). (B) TRV-based VIGS vector (Ratcliff et al., 2001). Ratcliff et al. constructed separate cDNA clones of TRV (strain PPK20) RNA1 and RNA2 under the control of cauliflower mosaic virus (CaMV) 35S promoters on the transferred (T) DNA of plant binary transformation vectors. They replaced the non-essential 29.4K and 32.8K genes with a multiple cloning site (MCS), leaving only the 5′ and 3′ untranslated regions and the viral coat protein. The cDNA clones were positioned between the left and right border (LB and RB) of the T-DNA and between CaMV 35S promoters (35S) and transcriptional terminators (T). The TRV open reading frames corresponded to the RdRp, MP, 16K, CP, and 29.4K and 32.8K proteins. (C) TRV-based VIGS vector (Liu et al., 2002a,b; Tian et al., 2014). TRV1: TRV cDNA clones were placed between the duplicated CaMV 35S promoter (2 × 35S) and the nopaline synthase terminator (NOSt) in a T-DNA vector. Rz, self-cleaving ribozyme. TRV2: TRV cDNA clones were placed between the duplicated CaMV 35S promoter (2 × 35S) and the nopaline synthase terminator (NOSt) in a T-DNA vector, and PDS was added to the MCS between CP and Rz. (D) Modified pTRV2 vector based on GATEWAY cloning technology containing attR1 and attR2 recombination sites (Liu et al., 2002a). The PCR products flanked by attB1 and attB2 sequences directionally recombined in vitro at the attR1 and attR2 sites contained in the plasmid when incubated with the BP CLONASE enzyme. Then, the PDS gene was cloned into the pTRV2-attR1-attR2 vector. (E) TRV-Ligation-independent cloning (LIC) vector (Dong et al., 2007). The TRV-LIC vector was created by inserting a cassette, containing adapters and two PstI sites, in two digestion and ligation reactions. Then, the CDS insely digested enzyme for digestion and ligation. (F) TRV-GFP vector (Tian et al., 2014). GFP CDS was fused with CP in the TRV2 vector to generate an easily traceable TRV vector in different parts of plants.