FIGURE 8.
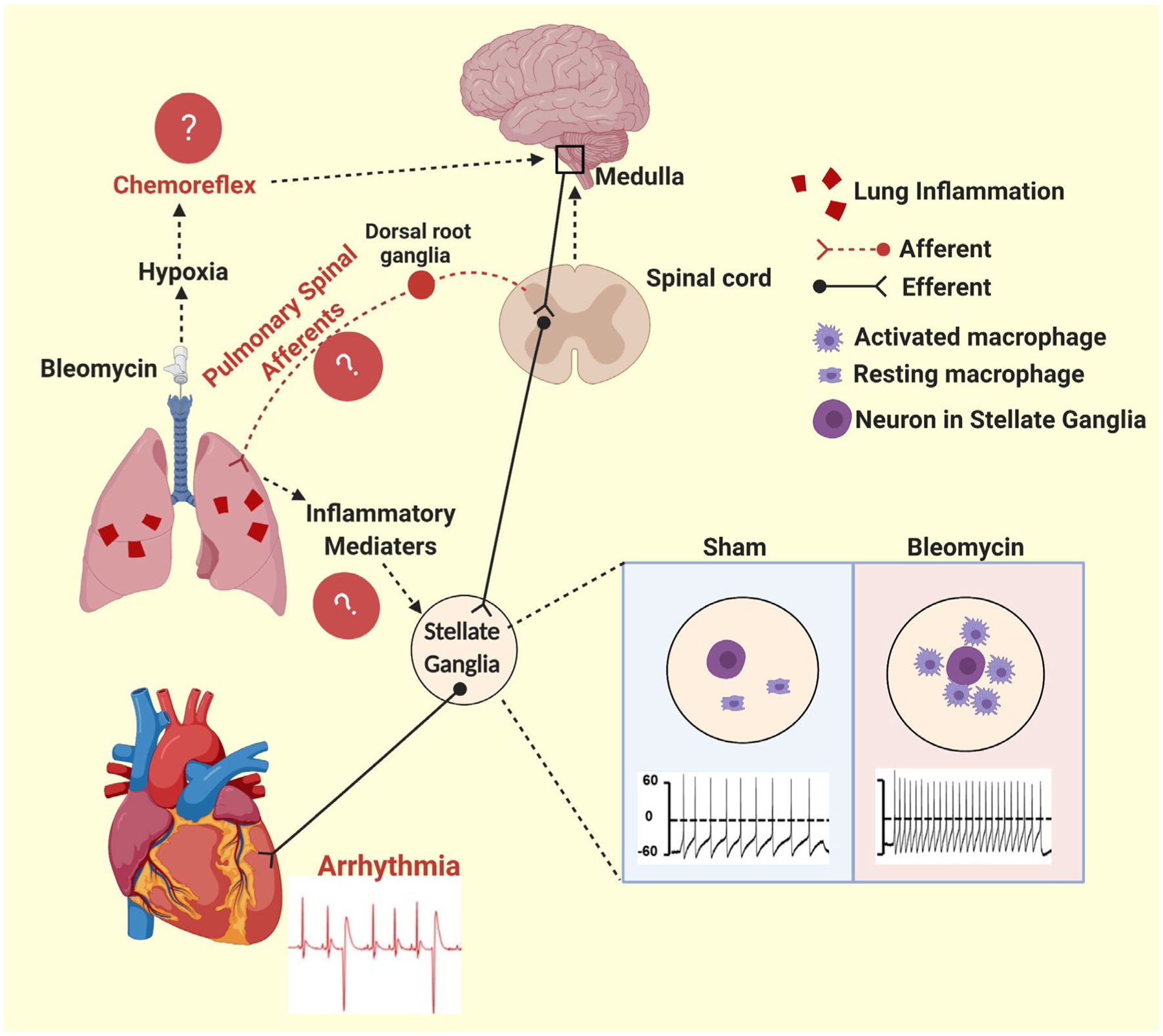
Schematic diagram showing that macrophage activation in the SG plays a critical role in mediating acute lung injury-associated cardiac arrhythmias. Following lung injury, we observed activated macrophages in the stellate ganglia and a significant increase in cardiac premature ventricular contraction (PVC). These increased PVCs are likely caused by a complex interaction between inflammation, the lung, the heart and the central and the peripheral nervous systems. The chemoreflex and PSAR may contribute to the cardiac phenotype. The data of this study suggest that neuroinflammation of the stellate ganglia contributes directly to this cardiac phenotype
