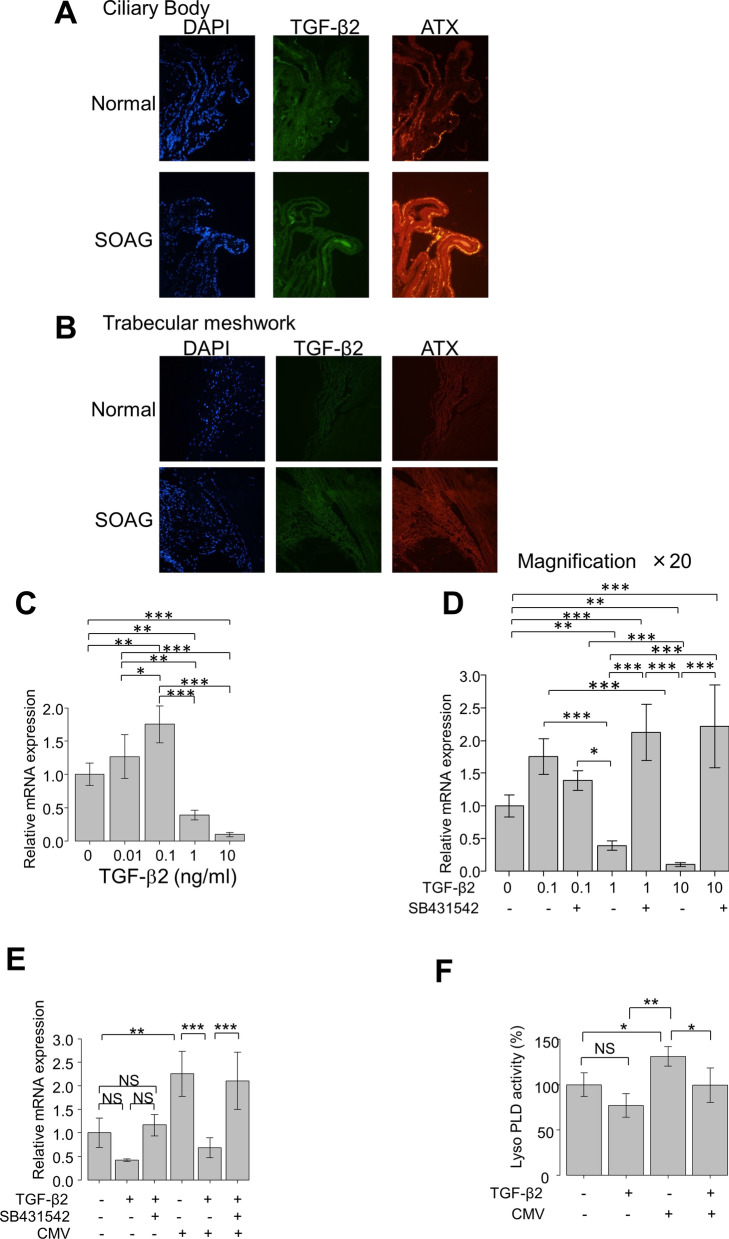
Fig. 2.
(A, B): RNAscope analysis of TGF-β2 and ATX mRNA expression levels in anterior segments of normal and SOAG eyes. Expression levels of TGF-β2 and ATX in CB (A) or TM (B) of normal and SOAG eyes. Both TGF-β2 and ATX mRNA expression levels were detectable in CB (A) and TM (B) in anterior segments of normal eyes. Expression levels of both TGF-β2 and ATX in CB were enhanced in SOAG eyes compared with normal eyes, while the expression level of ATX was elevated in CB of SOAG eyes (A). Expression levels of TGF-β2 and ATX in TM exhibited similar tendencies, and the expression level of ATX was also more robust than that of TGF-β2 in TM of SOAG eyes (B). C–F Effects of TGF-β2 on ATX mRNA expression level in hTM cells and LysoPLD activity in cell culture supernatant (n = 4). The relative mRNA expression level of ATX was significantly upregulated, compared with controls, following treatment with 0.1 ng/ml TGF-β2, but this upregulation was significantly suppressed by treatment with TGF-β2 at a concentration > 1 ng/ml (C). These effects were significantly suppressed by treatment with TGF-β inhibitor SB431542 (D). E Following treatment with TGF-β2 at a concentration of 500 pg/ml, the expression level of ATX was not significantly changed. The expression of ATX was significantly upregulated with CMV infection in the absence of TGF-β2, while the expression of ATX was significantly downregulated in the presence of 500 pg/ml TGF-β2. This downregulation was suppressed by treatment with TGF-β inhibitor (E). F LysoPLD activity in the conditioned medium was significantly upregulated by CMV infection, and suppressed by treatment with 500 pg/ml TGF-β2. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001