Figure 1.
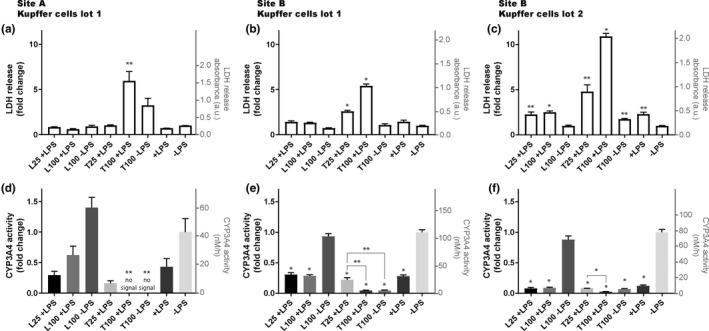
Toxic effects of trovafloxacin detected with PHHs co‐cultured with PHKCs in the liver MPS in two different experimental sites and using two validated lots of PHKCs. Site A was CN Bio Innovations in Cambridge, UK, and site B was FDA laboratories in Silver Spring, MD, USA. Trovafloxacin (T) and levofloxacin (L) were added to the cell culture medium of the liver MPS at a concentration of 25 or 100 µM in the presence (+) or absence (−) of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) at a concentration of 1 µg/ml to activate PHKCs. After 2 days of exposure, cell death was estimated by measuring LDH (a–c) and CYP3A4 activity (d–f) in the cell culture medium. Boxes represent average values and error bars represent the SEM. Identical lots of PHHs and PHKCs were used between site A (a, d) and site B (b, e). A separate lot of PHKCs was also used in site B (c, f). For each panel, *p < 0.005 and **p < 0.05 by unpaired t‐test with Welch’s correction. * and ** above column indicate statistical significance of difference relative to the control ‐LPS. Unless indicated otherwise, differences between values for presented conditions are not statistically different from the control ‐LPS. For (e) and (f), the statistical significance of differences between values of T25 +LPS condition and other conditions are also presented, such as T100 +LPS (e, f) and T100 ‐LPS (e). Three different wells were used per condition, except for experiments performed in site A, where 4 wells were used for condition L100 +LPS and T100 +LPS. LDH, lactate dehydrogenase; MPS, microphysiological system; PHHs, primary human hepatocytes; PHKCs, primary human Kupffer cells
