Figure 1.
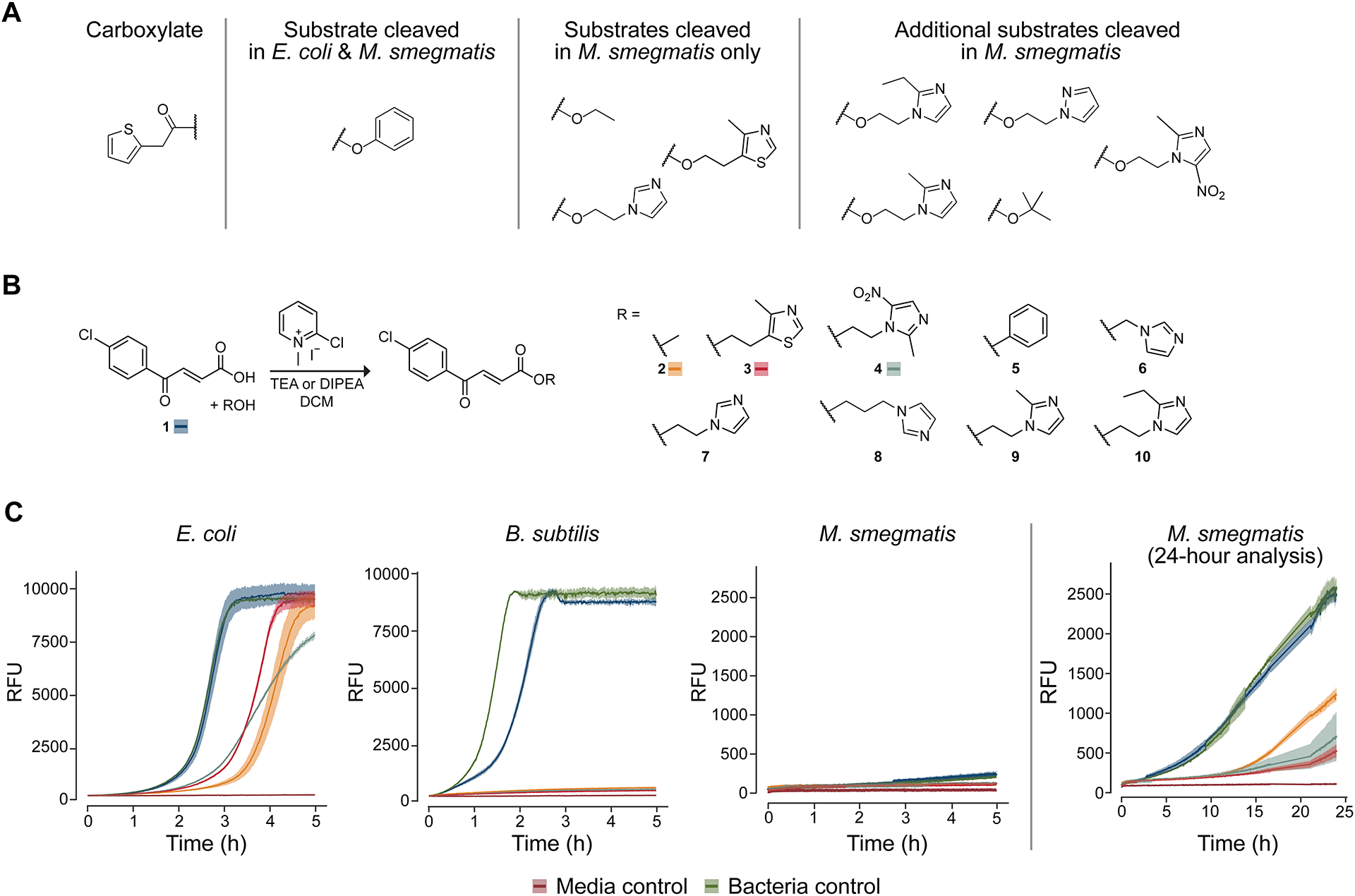
Microbial esterase activity assays. (A) A small panel of esters of 2-thiopheneacetic acid was assessed for cleavability in E. coli DH10B or M. smegmatis mc2155 lysate. Only the phenolic ester was cleaved in E. coli lysate whereas all four esters initially tested were cleaved in M. smegmatis lysate. Consequently, a larger panel of esters was screened in M. smegmatis lysate, and it was found that all esters were subject to cleavage. (B) Synthetic route to esters of trans-3-(4-chlorobenzoyl)acrylic acid. Note that acid 1 and esters 2–4 are labeled with the corresponding color for viability curves in panel C. (C) Viability curves for bacteria incubated with acid 1 and esters 2–4 (100 μM), which have high antimicrobial activity. Viability was assessed through the addition to the medium of resazurin dye, which fluoresces upon reduction in the presence of live, metabolizing cells. Medium: E. coli and B. subtilis, CAMHB; M. smegmatis, 7H9. Lines are the average of triplicate experiments; ribbons depict one standard deviation.
