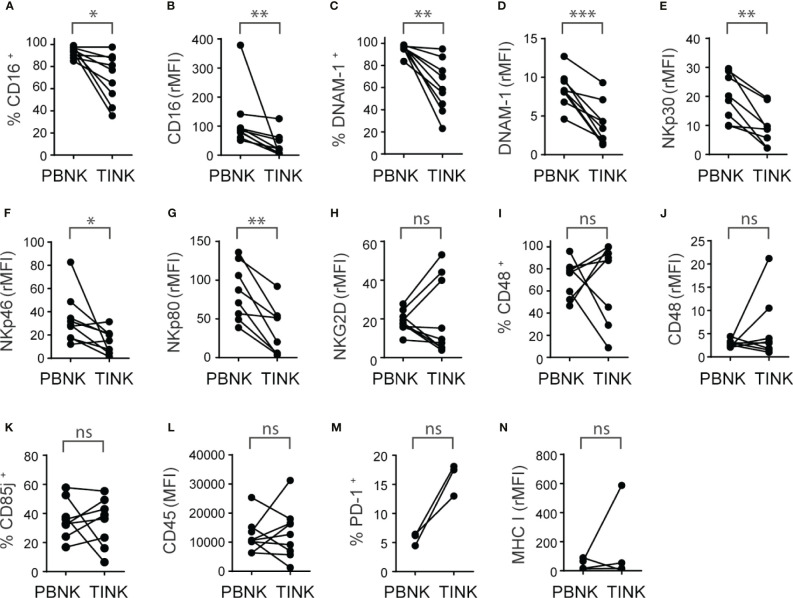
Figure 4.
TINK from ccRCC patients exhibit a similar increased expression of inhibitory receptors than PBNK and additional decreased expression of activating receptors. Peripheral blood NK cells (PBNK) and tumor-infiltrating NK cells (TINK) from ccRCC patients were analyzed by FC to compare the frequency of CD16+ cells (A), the intensity of expression of CD16 (B), the frequency of DNAM-1+ cells (C), the intensity of expression of DNAM-1 (D), the intensities of expression of NKp30 (E), NKp46 (F), NKp80 (G) and NKG2D (H), the frequency of CD48+ cells (I), the intensity of expression of CD48 (J), the frequency of CD85j+ cells (K), the intensity of expression of CD45 (L), the frequency of PD-1+ cells (M) and the intensity of expression of MHC-I (N). In (B, D–H, J, N), the relative MFI (rMFI) was used instead of MFI because the FMO was different for PBNK and TINK. n=9 (A–D, F, H, L); n=8 (E, G, I–K); n=3 (M); n=4 (N). A two-sided paired t-test was used in (A, D, E, G–I) and (K) A two-sided paired t-test with Wilcoxon rank test was used in (B, C, F, J, L, N). ns, not significant; *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001.