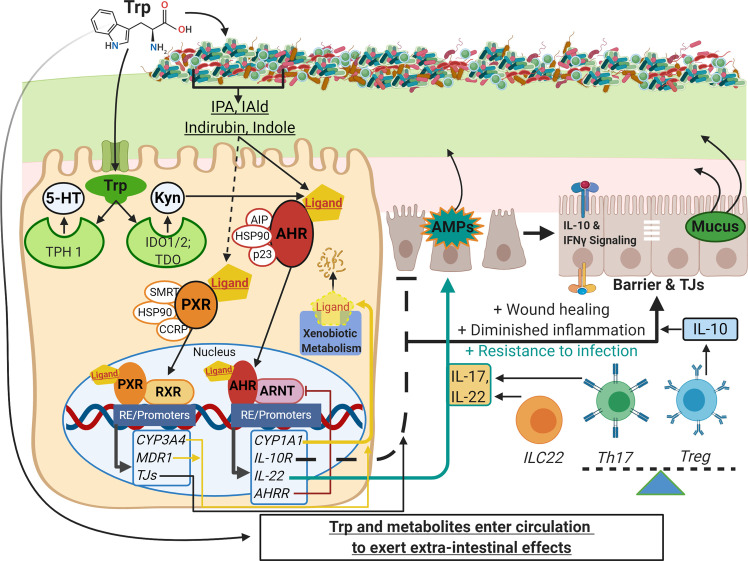
Figure 1.
Schematic of Trp metabolism, signaling pathways, and modulation of IEC and immune cell functions. On the left side, Trp enters host cells through various amino acid transporters and is metabolized endogenously: TPH1 (or TPH2 in the periphery) is the rate-limiting enzyme in conversion to 5-HT, and IDO and TDO enzymes convert Trp into Kyn. Gut microbes synthesize Trp de novo and convert this essential amino acid to numerous metabolites such as IPA, IAld, and indirubin. These metabolites, as well as endogenous Trp metabolites like Kyn, are shown to bind the ligand-activated transcription factor AHR and in some cases bind the transcription factor PXR. Both AHR and PXR are bound to chaperone proteins in the cytosol and ligand binding triggers nuclear translocation, heterodimer formation with either ARNT or RXR, respectively, and regulation of gene expression through heterodimer binding of response elements on various promoters throughout the genome (RE/Promoters). Genes upregulated by AHR and PXR include xenobiotic metabolizing enzymes (yellow lines), negative regulators (e.g. AHRR, red line), and effector molecules that modulate other pathways important in barrier function, dampening inflammation, and resistance to pathogens (black and teal lines; e.g. IL-10R, IL-22, IL-17). On the right side are other pathways involving IEC and immune cell functions that are influenced by Trp metabolite signaling: TJ formation, AMP and mucus secretion, IFN-γ signaling (influences IDO1 expression, alters Kyn metabolism and IL-10R expression), and the differentiation of immune cell subsets that regulate inflammatory responses (e.g. Th17, Treg and ILC22 cells). This image was created in BioRender.com. Trp, tryptophan; IEC,intestinal epithelial cells; TPH, tryptophan hydroxylase; 5-HT, serotonin; IDO, indolamine 2, 3-dioxygenase; TDO, tryptophan 2,3-dioxygenase; Kyn, kynurenine;IPA, indole-3-propionic acid; IAld, indole-3-carboxaldehyde; AHR, aryl hydrocarbon receptor; PXR, pregnane X receptor; ARNT, AHR nuclear translocator; RXR,retinoid X receptor; AHRR, AHR repressor; TJ, tight junctions; AMP, antimicrobial peptides; Th and Treg, helper and regulatory T cells, respectively.