Fig. 1. Routes to HJ formation and the proteins that promote or nullify each.
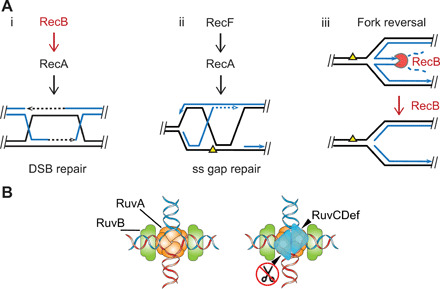
(A) HJ-generating processes and E. coli protein players: (i and ii) HR [reviewed in (4)] and (iii) RecBCD removal or prevention of reversed forks by its specific degradation of double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) ends, shown by Michel and colleagues (6, 15). Notched circle RecB indicates RecBCD nuclease, close parallel lines indicates base-paired DNA strands, and dashed lines indicates DNA repair synthesis. (B) Illustration of RuvCDef (blue triangles) binding to an HJ, taken from Xia et al. (5) (published under a CC BY-NC license, https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/).
