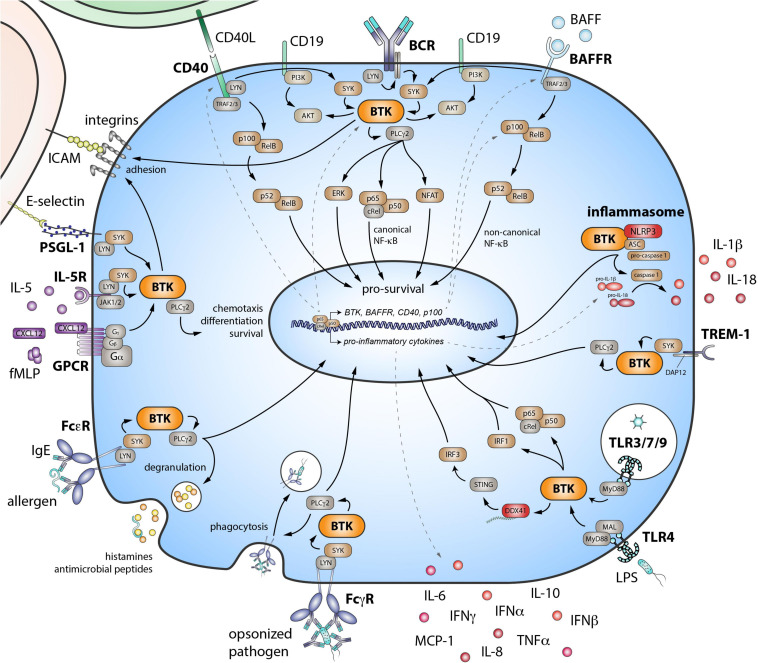
FIGURE 1.
Role of Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK) in various signaling pathways in B cells and myeloid cells. BTK is critical downstream of the B cell receptor (BCR). The BAFF receptor (BAFFR) transduces signals by coopting the BCR. The co-stimulatory receptor CD40 also signals via both the noncanonical NF-κB pathway and BTK. Eventually, these signaling pathways lead to the activation of downstream transcription factors—important for survival, differentiation, proliferation, and cytokine production of B cells. BTK also functions in inflammasome activation and in signaling downstream pattern recognition receptors, including triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 1 (TREM-1) and the Toll-like receptor (TLR) family. Activating FcγRs via BTK signaling, can stimulate cells to initiate cytokine production, phagocytosis, and microbicidal activity of engulfed pathogens. FcεRs can bind IgE and are mostly expressed on mast cells and basophils. When cross-linked, these receptors also signal via BTK, resulting in the quick release of histamines and antimicrobial peptides via degranulation. BTK is also involved in downstream signaling of G-protein coupled receptors (GPCR), such as chemokine and cytokine receptors. E-selectin–driven engagement of PSGL-1 induces downstream signaling via BTK to activate integrins. SYK, spleen tyrosine kinase; PLCγ2, phospholipase Cγ2; PI3K, phosphoinositide 3-kinase; ERK, extracellular signal-regulated kinase; NF-κB, nuclear factor-κB; TRAF, tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor; BAFF, B cell activating factor of the tumor necrosis factor superfamily; NLRP3, NLR family pyrin domain containing 3; ASC, apoptosis-associated speck like protein containing a caspase recruitment domain; DAP12, DNAX activation protein of 12 kDa; MyD88, myeloid differentiation primary response 88; MAL, MyD88 adaptor-like; IRF, interferon regulatory factor; DDX41, DEAD-box helicase 41; STING, stimulator of interferon genes; IL, interleukin; IFN, interferon; MCP-1, monocyte chemoattractant protein-1; TNFα, tumor necrosis factor α; FcγR, Fcγ receptor; FcεR, Fcε receptor; fMLP, N-Formylmethionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine; CXCL12, C-X-C-motif chemokine ligand 12; JAK, Janus kinase; PSGL-1, P-selectin glycoprotein ligand-1; ICAM, intercellular adhesion molecule.