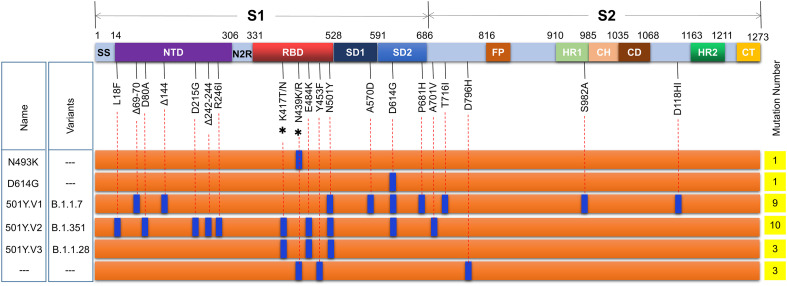
Fig. 1.
Major mutations in the spike protein of SARS-CoV-2. To date, more than 3698 mutations in the S protein were identified, including 2746 mutations causing amino acid changes, of which more than 340 amino acids are located in the viral RBD. Among these mutations, the most representative ones are substitution mutations such as D614G, N501Y, Y453F, N439K/R, P681H, K417N/T, and E484K, and deletion mutations of ΔH69/V70 and Δ242–244. Three mutations, D614G, N501Y, and E484K, confer the virus with enhanced infectivity, transmissibility, and resistance to neutralization. Δ, deletion; *, two meaningful mutations at this site; −--, unidentified mutations. Signal sequence (SS), NTD (N-terminal domain), N2R (NTD-to-RBD linker), RBD (receptor-binding domain), SD1 and SD2 (subdomains 1 and 2), FP (fusion peptide), HR1 (heptad repeat 1), CH (central helix), CD (connector domain), HR2 (heptad repeat 2), and CT (C-terminal domain).