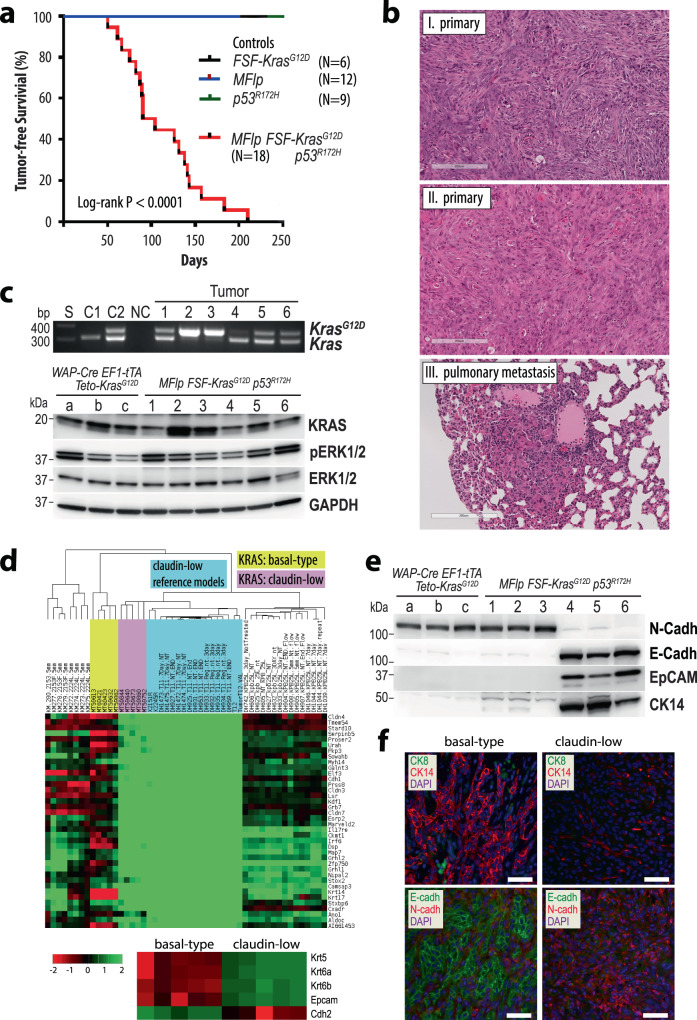
Fig. 5. A gain-of-function mutation of endogenous Kras in the mammary epithelium results in the development of basal-like and claudin-low mammary cancers.
a Kaplan-Meier survival plot of mice that expresses KRASG12D from the endogenous Kras gene in an Flp-recombinase-inducible manner in the presence of a mutant p53R172H allele (MMTV-Flp FSF-KrasG12D p53R172H). Statistical significance in tumor-free survival between control and experimental animals was calculated with the log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test. The resulting P-value was <0.0001 (Chi square = 34.35). b Histological sections of primary mammary tumors (N = 10 biological replicates) and a pulmonary metastatic lesion (N = 6 biological replicates). c Top panel: PCR-based validation of the Flp-mediated excision of the Frt-Stop-Frt (FSF) sequence in the targeted FSF-KrasG12D allele (N = 6 biological replicates); S, DNA ladder: C1 and C2 tail DNA of mice that carry two wildtype Kras alleles (C1) or one FSF-KrasG12D allele (C2); NC, no DNA control. Bottom panel: Immunoblot analysis to compare the expression of KRAS and activation of MAP kinases in mammary tumors that originated in mice with exogenous mutant KRAS expression (samples a–c, N = 3 biological replicates) with mammary tumors expressing endogenous KRASG12D (samples 1–6 corresponding to the PCR panel above, N = 6 biological replicates). Note that mice 1–6 carried one FSF-KrasG12D and one wildtype Kras allele. Therefore, the loss of the wildtype Kras allele in tumor samples 2 and 3 occurred somatically. d RNA sequencing-based gene expression and cluster analysis to compare the molecular profiles of mammary tumors expressing endogenous KrasG12D (N = 10 biological replicates) with reference sets from diverse mammary cancer models. The bottom panel illustrates the differences in the expression of basal-type keratins (Krt5, Krt6a/b), Epam, and N-cadherin (Cdh2) between mutant KRAS expressing tumors that exhibit similarities to basal-like or claudin-low molecular subtypes. e Immunoblot analysis of E-cadherin and N-cadherin, EpCam, and CK14 expression on the same mammary tumors shown in panel c. f Immunofluorescent staining of CK8, CK14, as well as E-cadherin and N-cadherin on sections from basal-like (N = 5 biological replicates) or claudin-low tumors (N = 5 biological replicates); bars, 50 µm.