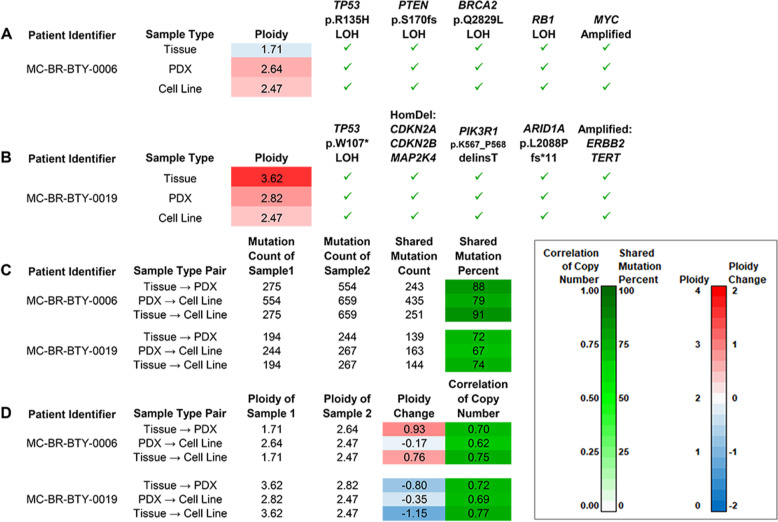
Fig. 5. Exome sequencing reveals several patient-specific cancer driver mutations and an evolutionary trajectory that features their preservation in the presence of somatic changes suggestive of genome instability.
A Oncogenic mutations in five cancer genes were detected in all three MC-BR-BTY-0006 tumor samples. Pathogenic loss-of-function somatic SNVs were detected in one allele of each of the genes TP53, PTEN, and BRCA2 as well as the other allele (loss of heterozygosity, or LOH). Thus, loss of function of both copies of tumor-suppressor genes TP53, PTEN, and BRCA2 could be inferred. RB1 loss of heterozygosity (LOH) and amplification of MYC were other oncogenic events observed. B Oncogenic mutations in eight cancer genes were detected in all three MC-BR-BTY-0019 tumor samples. A different pathogenic loss-of-function mutation in TP53 for cell line, but was again observed alongside LOH. So, loss of function of both copies can be inferred for TP53 as well as for three other tumor suppressor genes, CDKN2A, the adjacent CDKN2B, and MAP2K4, due to homozygous deletion (HomDel). Mutations were also observed in PIK3R1 and ARID1A. The mutations affect sites in regions frequently altered in cancer. Amplifications of TERT and ERBB2, or HER2, were also detected, with particularly high amplification for ERBB2. C Of the somatic SNV/INDELs detected in the patient tumor tissue samples, proportions detected in PDXs and cell lines were high (≥72%) for both patients. Of those mutations detected in PDXs, proportions detected in cell lines were also high (79%, 67%). D Changes in ploidy by sample type pair. For each patient, the absolute differences were nearly 1 copy from tissue to PDX with a Tissue→PDX increase observed for MC-BR-BTY-0006 and a Tissue→PDX decrease observed for MC-BR-BTY-0019. Despite these changes, the profiles of within-sample relative copy numbers for Tissue and PDX still showed similarity as the correlation of copy number was still 0.70 or greater. Slight decreases in ploidy were observed from PDX to cell line for both patients.