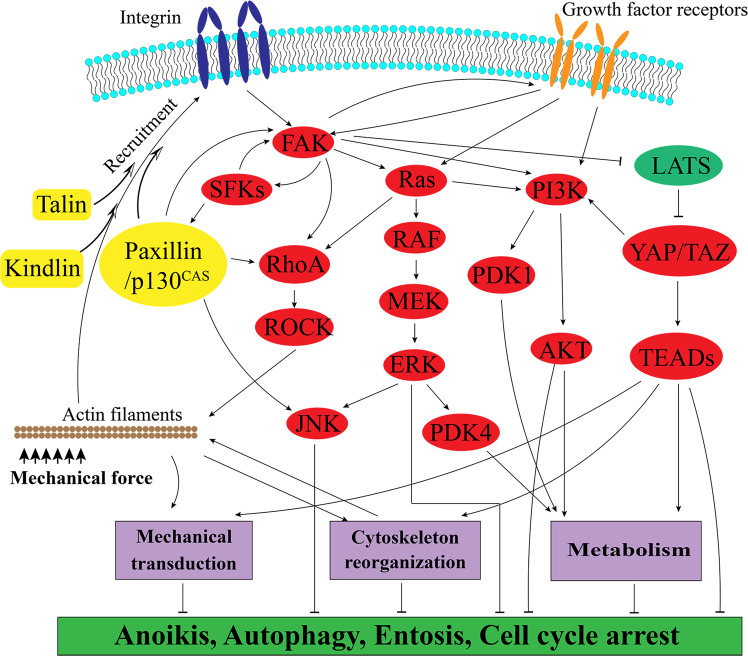
Fig. 2. Molecular pathways sustaining anchorage-independent survival.
During detachment, the ligand–integrin interaction between cells and ECM is disrupted and the cells lose the growth stimuli from ECM. However, the integrin can be also stimulated by mechanical force and cytoskeleton reorganization that actin filaments recruit integrin adaptor proteins, such as talin, kindlin, paxillin, and p130CAS to integrin, hence inducing integrin clustering and activation. The activated integrin induces FAK/SFK activation and its downstream signaling proteins. There is also crosstalk between FAK/SFK and growth receptor signaling, such as EGFR, PDGFR, VEGFR, and IGFR signaling pathway. In cooperation with growth receptor signaling, integrin/FAK/SFKs induces Paxillin/p130CAS/JNK, Ras/ERK, PI3K/AKT, YAP/TAZ, and RhoA/ROCK signaling activation, and hence regulate mechanical transduction, cytoskeleton reorganization, and metabolism. Noteworthy, there is also crosstalk between these downstream signaling pathways. Eventually, activated integrin signaling and its downstream signaling inhibits various forms of cell death, including anoikis, autophagy, cell cycle arrest and entosis.