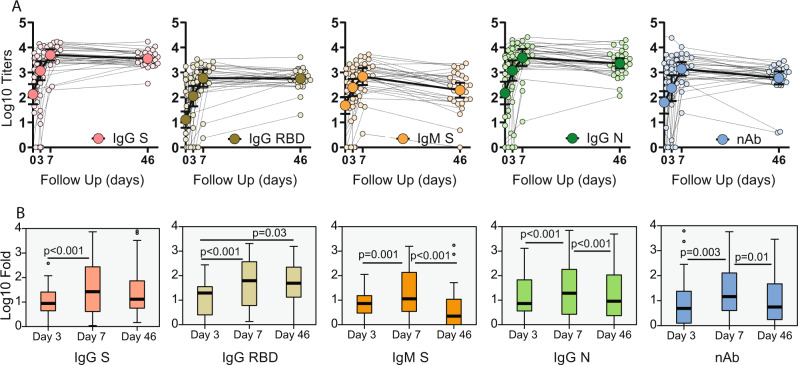
Fig. 1. Longitudinal antibody response to SARS-CoV-2 antigens.
Serum from hospitalized COVID-19 patients was analyzed at baseline, at hospital recruitment and days 3 and 7. A subsequent sample was collected in the convalescence period in the COVID-19 survivors with mean time of 46 days. A Longitudinal profile of antibodies against SARS-CoV-2. Antibody titer was quantified as area under the curve (AUC) after serial serum dilution for each sample (Supplementary Fig. 1). Calculated AUC at each time is shown to quantify changes over time for each individual (small dots) against immunoglobulin G (IgG) spike, IgG receptor-binding domain (RBD), immunoglobulin M (IgM) spike and IgG nucleocapsid (N); and neutralizing activity (nAb) as inhibitory concentration 50% (IC50%). Geometric mean titer (GMT, big dots) and confidence interval (CI 95%) are also shown. B Boxplot diagram of geometric mean fold rise (GMFR) antibody titers against SARS-CoV-2 at the same time points: IgG spike, IgG RBD, IgM spike and IgG NP; and neutralizing activity (nAb). Related-samples Friedman’s two-way ANOVA was performed. Significant adjusted p values after pairwise comparisons are shown for each comparison. Black bar indicates GMFR values, box indicates IQR (Q1–Q3), lines indicate minimum and maximum. Outliers from the observed distribution are shown. Total n = 116 biologically independent serum samples (day 0 = 37, day 3 = 29, day 7 = 22, day 46 = 28). n = 116 biological samples examined against four different SARS-CoV-2 substrates for ELISA assays; ELISAs for each substrate were run once each. N = 116 serum samples examined over two independent experiments for neutralization assays.