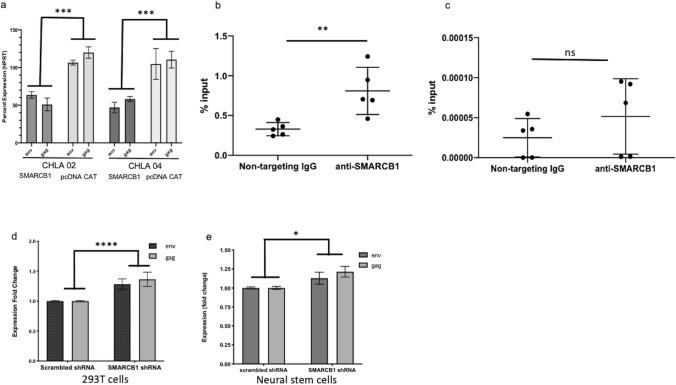
Figure 3.
SMARCB1 regulates HERV-K (HML-2) env expression. (a) Restored SMARCB1 expression in CHLA 02 and CHLA 04 AT/RT cell lines results in downregulation of HML-2 transcription measured at 48 h by qRT-PCR. (b,c) SMARCB1 binds the HML-2 LTR significantly more than the promoter of control gene, HPRT. (b) SMARCB1 transfected 293 T cells show a significantly greater proportion of HML-2 LTR bound to SMARCB1 following immunoprecipitation compared to control, non-targeting IgG. (c) SMARCB1 transfected 293 T cells show no significant difference between non-targeting IgG bound to genomic HPRT and SMARCB1 bound to genomic HPRT. Percent input is a normalized value with input set to 100% (e.g. % input = 100*2^(input Ct − immunoprecipitated chromatin Ct). Ct is cycle threshold. (d,e) SMARCB1 knockdown results in increased transcription of HML-2 transcripts as measured with qRT-PCR. (d) HML-2 transcripts in 293 T cells transfected with scrambled shRNA control compared to shRNA targeting SMARCB1 at 24 h as measured by qRT-PCR. (e) HML-2 transcripts in neural stem cells transfected with scrambled shRNA control are significantly higher compared to transcripts in cells transfected with shRNA targeting SMARCB1 at 48 h. (qRT-PCR) Data was entered into Prism v9 for graph creation. [Error bars represent SEM. Statistics in Supplemental Table S6].