FIGURE 4.
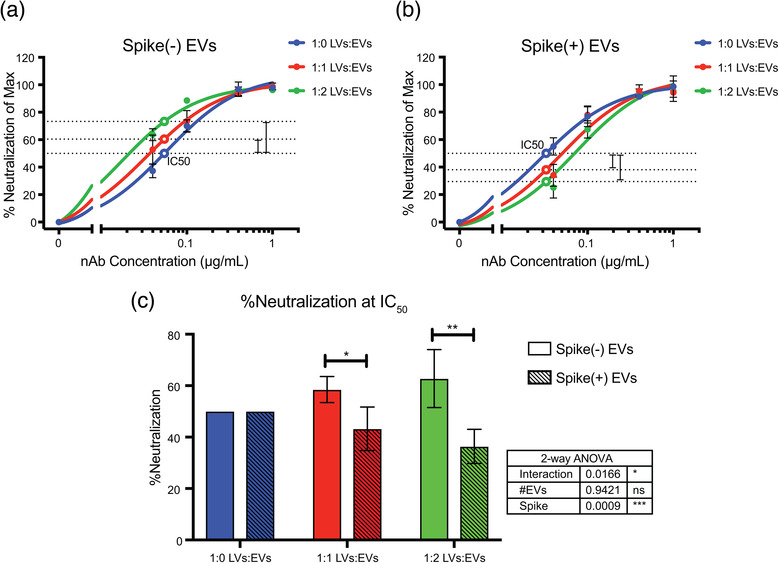
Spike(+) EVs reduce the efficiency of commercial neutralizing antibodies at blocking SARS‐CoV‐2 spike‐dependent viral entry. Representative dose curves of nAb‐mediated inhibition of S‐LV entry in the presence of spike(‐) EVs (a) and spike(+) EVs (b) at varying ratios. Data are displayed as mean ± SD of technical triplicates. The open point on the blue line (1:0 LVs:EVs) represents the interpolated IC50 value. The open points on the red and green lines represent the interpolated % neutralization value at the IC50 concentration determined from the blue line. Dashed lines are a visual representation of the changes in neutralization efficiency induced by spike(‐) or (+) EVs. (c) Summary data from three independent biological replicates of nAb efficacy in the presence of spike(‐) and spike(+) EVs. Data are displayed as mean + SD of three independent biological (n = 3) experiments. Solid filled columns are spike(‐) EVs and dashed fill columns are spike(+) EVs. Significance was measured by two‐way ANOVA followed by Sidak's multiple comparisons test. Inset table displays ANOVA p‐values and contributions of variables to overall variance. Asterisks over the columns represent the P‐values of the multiple comparisons tests. *, P ≤ 0.05; **, P ≤ 0.01; ***, P ≤ 0.001
