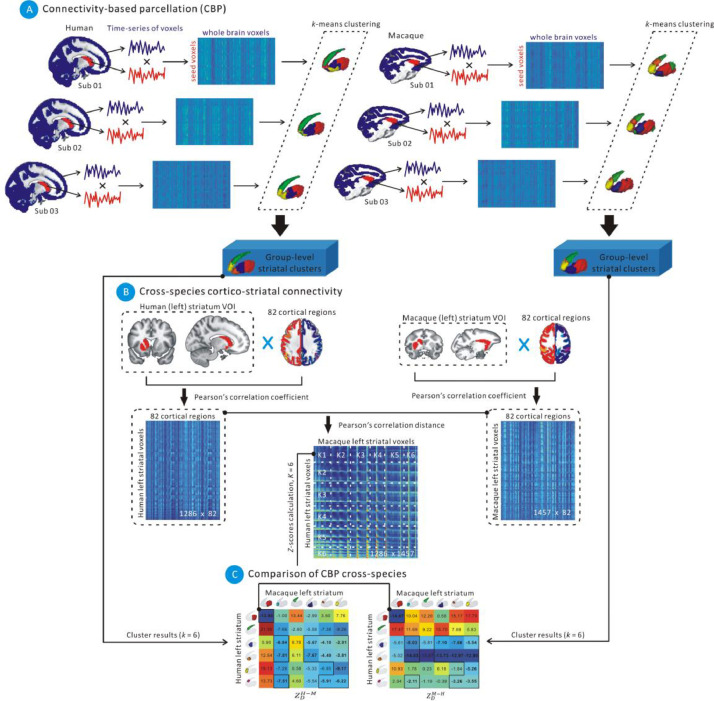
Fig. 1.
A sketch of our proposed pipeline depicting its use on the left striatum. (A) Connectivity-based parcellation (CBP) of human and macaque striatum based on the RSFC between the striatal voxels and whole-brain gray matter voxels. Each subject's RSFC connectivity matrix is then subjected to k-means clustering while varying number of clusters. The final number of clusters was selected using several data-driven model selection criteria. The subject-level clusters where then aggregated into group-level clustering for humans and macaques separately. (B) Cross-species cortico-striatal connectivity: The RSFC between striatal voxels and regions of regional map (RM) was calculated for each subject and then averaged. The distance between each human striatum voxel and each macaque striatum voxel was calculated using the Pearson correlation (1-R) between the corresponding RM connectivity profiles. (C) Comparison of CBP-derived parcels cross-species. The permutation based Z-scores were calculated for comparing the cortico-striatal RSFC of the CBP-derived parcels (shown here for k = 6).