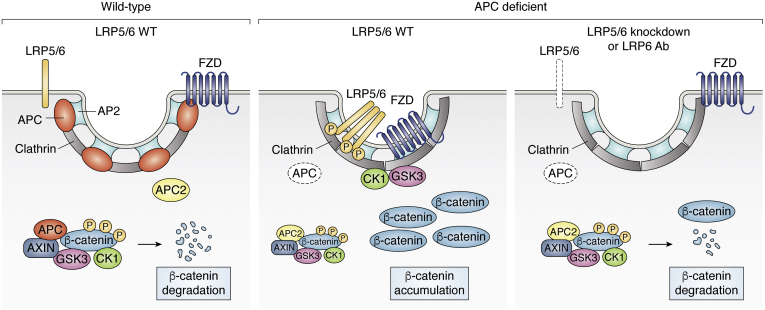
Figure 4.
APC-deficiency induces Wnt signaling through the clathrin endocytic pathway.Left, in wild-type cells, APC works with axin, GSK3, and CK1 to degrade β-catenin protein and binds to clathrin to suppress Wnt-independent signalosome assembly. Middle, when APC is knocked down (or mutated), APC2 cannot compensate for APC to suppress signalosome formation, which leads to β-catenin protein accumulation in the cell. Right, in the events of LRP knockdown or treatment with LRP6 antibody or with FZD or DVL antagonists, the signalosome is no longer active, and the APC2-mediated destruction complex continues to degrade β-catenin, which leads to much suppressed Wnt/β-catenin signaling (right panel). APC, adenomatous polyposis coli; CK1, casein kinase 1; DVL, Dishevelled; GSK3, glycogen synthase kinase 3; LRP6, low-density lipoprotein receptor-related proteins 6.