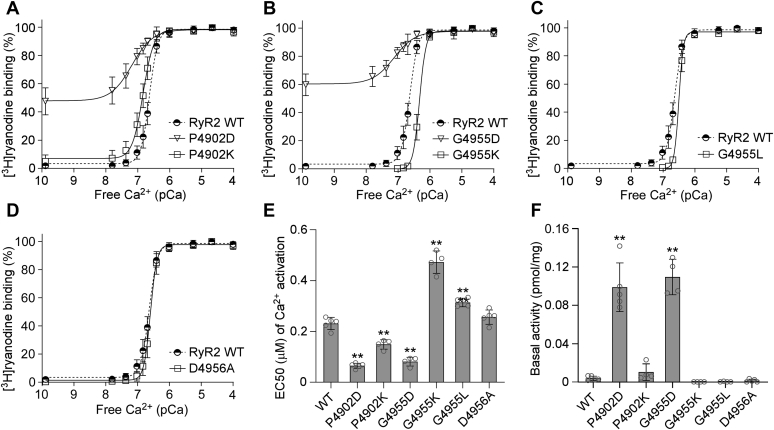
Figure 7.
Effects of CTD mutations on [3H]ryanodine binding to RyR2. [3H]ryanodine binding to cell lysate prepared from HEK293 cells transiently transfected with the RyR2 WT or CTD mutant complementary DNAs was carried out at various Ca2+ concentrations (0.1 nM–0.1 mM). The amounts of [3H]ryanodine binding at various Ca2+ concentrations were normalized to the maximal binding (100%). [3H]ryanodine binding to RyR2 WT, P4902D, P4902K (A), to RyR2 WT, G4955D, G4955K (B), to RyR2 WT, G4955L (C), or to RyR2 WT and D4956A (D). EC50 values of Ca2+ activation (one-way ANOVA with Dunnett's post hoc test, F = 142.7, p < 0.0001) (E) and basal activity (in the near absence of Ca2+, ~0.1 nM) (F) of [3H]ryanodine binding to RyR2 (one-way ANOVA with Dunnett's post hoc test, F = 71.9, p < 0.0001). Data shown are mean ± SD from four to five separate experiments. ∗∗p < 0.01 versus WT. CTD, C-terminal domain; HEK293, human embryonic kidney 293 cells; RyR2, cardiac ryanodine receptor.