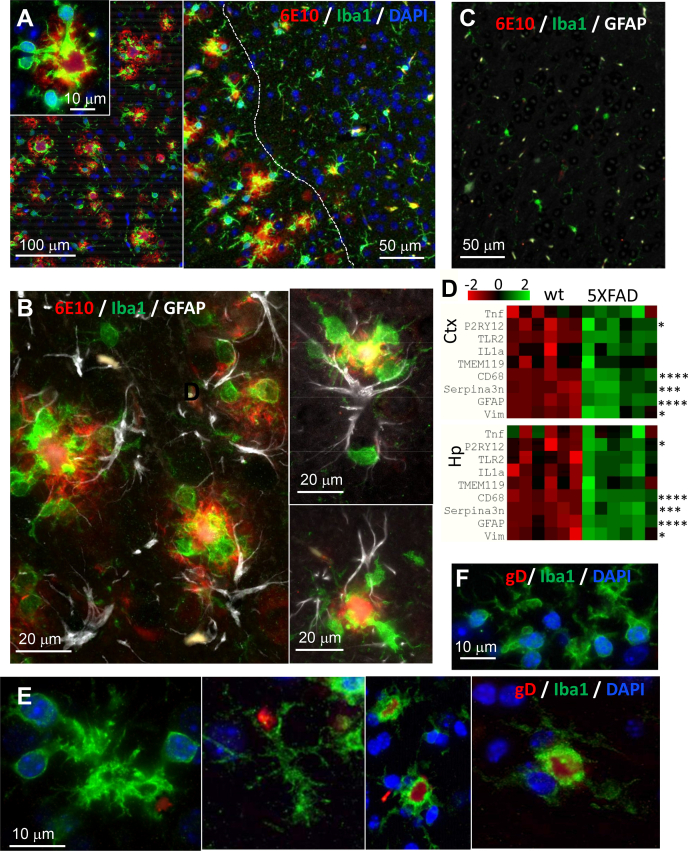
Figure 11.
Reactive microglia are primed for phagocytosis in the areas with high density of Aβ aggregates in aged 5XFAD mice.A–C, coimmunostaining for Aβ aggregates (6E10 antibody, red), reactive microglia (anti-Iba1 antibody, green), and nuclei (DAPI, blue) (A), or Aβ aggregates (6E10 antibody, red), reactive microglia (anti-Iba1 antibody, green), and reactive astrocytes (anti-GFAP, Millipore, white) (B and C) of motor cortices of 10-month-old 5XFAD mice (A and B) or WT littermates (C). The dashed line in panel A separates areas with a high density of Aβ aggregates. D, heatmap analysis of the expression of genes that reports on reactive state of microglia and astrocytes in cortex (Ctx) and hippocampus (Hp) of 10-month-old 5XFAD mice (n = 6 mice) and WT littermates (n = 6 mice). Differential expression p-values were calculated with nCounter Advanced Analysis and are adjusted for false discovery rate (Benjamini–Yekutieli method), ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001. E and F, coimmunostaining for HSV-1 (gD antibody, red), reactive microglia (anti-Iba1 antibody, green), and nuclei (DAPI, blue) in motor cortices of 10-month-old 5XFAD mice infected IC with 104 PFUs of McKrae and examined 24 h postinfection (n = 5 mice). E, and uninfected age-matched 5XFAD (n = 2 mice) (F).