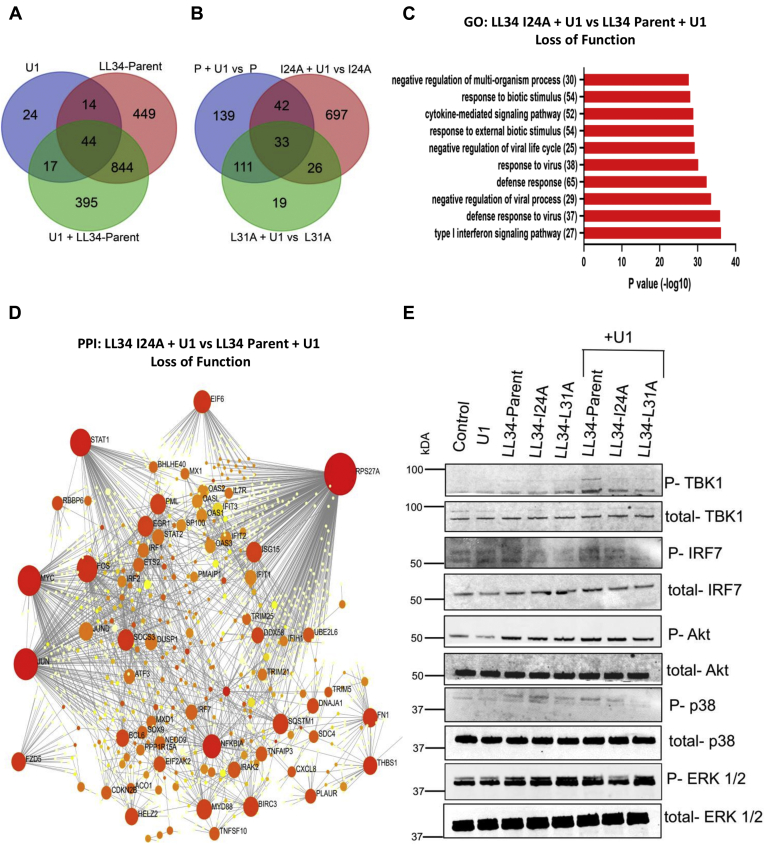
Figure 3.
LL-34 I24A and L31A mutations result in loss of innate immune vetting of U1 dsRNA leading to repressed activation of antiviral and innate immune pathways.A, Venn diagram for all differentially expressed genes from NHEKs treated with U1 dsRNA, LL-34-parent, and combinations of either U1 dsRNA and LL-34-parent. B, Venn diagram for showing genes differentially regulated in cells treated with U1 dsRNA and LL-34-I24A versus LL-34-I24A and U1 dsRNA and LL-34-L31A versus LL-34-L31A mutants in comparison to U1 dsRNA and LL-34-parent versus LL-34-parent as shown. C, gene ontology (GO) pathway analysis of genes downregulated in cells cotreated with U1 dsRNA and LL-34-I24A versus U1 dsRNA and LL-34-parent. D, protein–protein interaction networks were derived from cells cotreated with U1 dsRNA and LL-34 I24A mutant peptide and compared with cells treated with U1 dsRNA and LL-34 parent. Red seeds indicate genes that form over-represented networks and are indispensable. E, NHEKs were treated with U1 dsRNA (2.5 μg/ml) and/or LL-34-parent, LL-34-I24A, and LL-34-L31A (2 μM). Protein expression of p-TBK1, TBK1, p-IRF7, IRF7, p-Akt, Akt, p-ERK1/2, and ERK1/2 was assessed with immunoblot. ERK1/2, extracellular signal–regulated protein kinase; IRF7, interferon regulatory factor 7; LL-34, 34-amino acid peptide; NHEKs, normal human epidermal keratinocytes; TBK1, TANK-binding kinase 1.