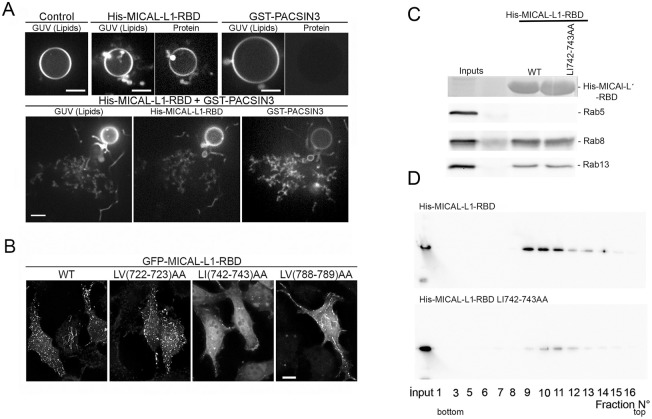
Fig. 5.
Two amino acids in MICAL-L1-RBD domain are important for PA binding and association with membrane tubules. (A) In vitro tubulation assays were performed with fluorescent PA-containing GUVs and His-MICAL-L1-RBD coupled to AlexaFluor 488 or GST-PACSIN3-AlexaFluor 647. After incubation, samples were imaged by video spinning confocal microscopy. Images were collected at 100-ms intervals (50-ms exposure per channel) using the same illumination and gain conditions. Images for GUV alone (control), GUV incubated with His-MICAL-L1-RBD, GST-PACSIN3, and His-MICAL-L1-RBD plus GST-PACSIN3. Scale bars: 5 µm. (B) Coverslips of HeLa cells expressing GFP-MICAL-L1-RBDWT, GFP-MICAL-L1-RBD LV (722-723) AA, GFP-MICAL-L1-RBD LI (742-743) AA and GFP-MICAL-L1-RBD LV (788-789) AA mutants were analyzed by immunofluorescence. 3D projections of images are shown. Scale bar: 10 µm. Note that mutations of LI742-743AA impairs MICAL-L1 tubulo-vesicular distribution. (C) Purified His-MICAL-L1 RBDWT and LI742-743AA bound to Nickel beads (coomassie staining) were incubated with HeLa cell extract to pulldown endogenous Rab5 (negative control), Rab8 and Rab13. Bound proteins were analyzed by immunoblotting using anti- Rab5, Rab8 and Rab13 antibodies. (D) Equal amounts of purified His-MICAL-L1-RBD WT and LI742-743 mutant proteins were incubated with liposomes enriched in PA, and then subjected to a flotation assay. Different fractions were collected and analyzed by blotting using anti-His for MICAL-L1 RBD detection. Note that Leu-Ileu742-743AA mutant reduces PA binding.