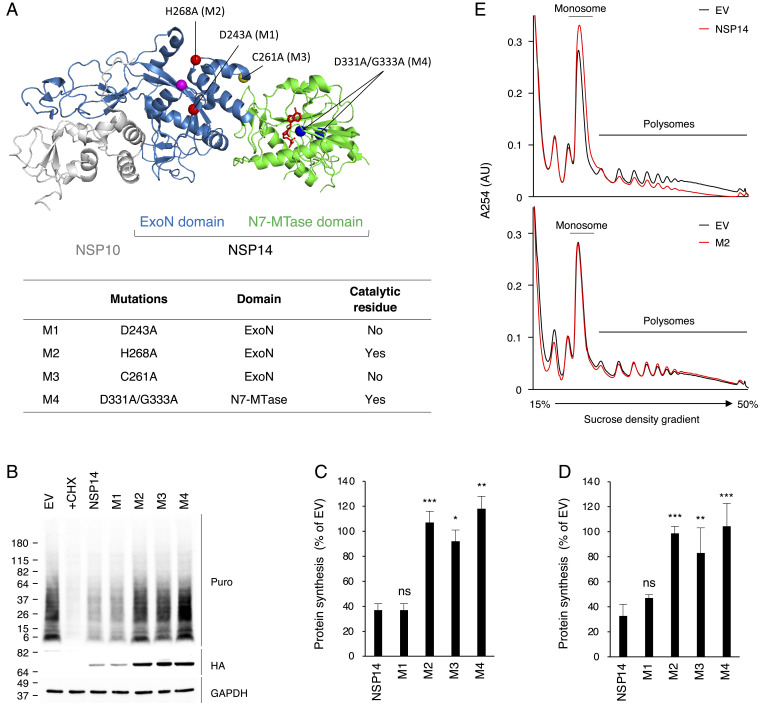
Fig. 4.
ExoN and N7-MTase are required for translation inhibition activity of NSP14. (A) Crystal structure of SARS-CoV NSP10−NSP14 complex (Protein Data Bank ID code 5NFY). NSP10 is shown in gray. N-terminal ExoN and C-terminal N7-MTase domains are in blue and green, respectively. NSP14 mutants are described below, in the table. The mutation residues are highlighted in the structure. (B) The 293T cells were transfected with plasmids encoding WT or NSP14 mutants for 24 h and puromycin labeled for 15 min. Puromycin incorporation was determined by immunoblotting using anti-puromycin antibody (Puro). HA-tagged NSP14 proteins were detected by anti-HA antibody (HA). (C) Quantification of puromycin incorporation assay shown in B. (D) The 293T cells were transfected with plasmids encoding WT or NSP14 mutants. After 24 h of transfection, cells were pulse labeled with OP-Puro for 1 h, fixed, fluorescently labeled, and analyzed by FACS. (E) The 293T cells were transfected with plasmids encoding NSP14 or M2 mutant for 24 h. Cell lysates were cleared by centrifugation, loaded onto a 15 to 50% sucrose gradient, and subjected to ultracentrifugation. Absorbance was monitored at 254 nm to record the polysome profile. The monosome and polysome pools are indicated. For C and D, data are shown as mean ± SD of three biological repeats. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 by unpaired Student’s t test.