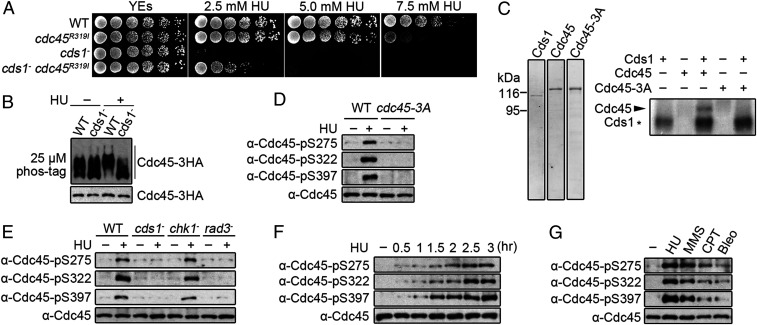
Fig. 1.
Cds1Chk2 phosphorylates Cdc45 on S275, S322, and S397 when replication forks stall. (A) A fivefold serial dilution of the indicated stains grown with the designated concentration of HU. (B) Cdc45 phosphorylation in response to HU. (Top) Phos-tag sodium dodecyl sulphate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE). (Bottom) SDS-PAGE. HA-tagged Cdc45 was detected by α-HA. (C, Left) Purified Cds1, Cdc45-MBP-tag, and Cdc45-S275A-S322A-S397A (S3A). (Right) Autoradiograph of purified Cdc45 following in vitro phosphorylation by Cds1Chk2. (D) Detection of Cdc45 phospho-S275, -S322, and -S397 in vivo using phospho-specific antibodies. (E) Phosphorylation of Cdc45 S275, S322, and S397 in the indicated strains. (F) Time course of S275, S322, and S397 phosphorylation following HU treatment. (G) Cdc45 phosphorylation in response to the indicated genotoxic agents.