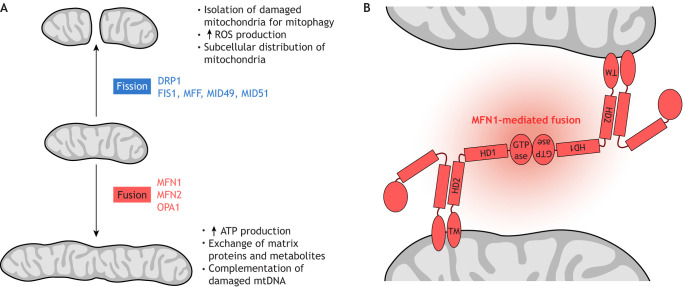
Fig. 1.
Mitochondrial fusion and fission. (A) Factors involved in these processes and effects on mitochondrial activity. (B) Mitofusin 1 (MFN1)-mediated fusion between two outer mitochondrial membranes. Mitofusins are dynamin-related GTPases essential for mitochondrial fusion, which in turn is crucial for physiological mitochondrial function. Importantly, fusion allows complementation of damaged mtDNA (Nakada et al., 2001). Fusion defects cause neurologic disease (see Table 1). MFN1 is comprised of an N-terminal GTPase domain and two coiled-coil heptad-repeat regions (HR1 and HR2) that are separated by two adjacent small transmembrane domains. This model is based on crystal structures of a truncated version of MFN1 lacking the C-terminal part of the HR1 domain, the transmembrane domain (TM) and the N-terminal part of the HR2 domain (see Cao et al., 2017; Qi et al., 2016). ATP, adenosine triphosphate; GTPase, guanosine triphosphate hydrolysis domain; HD1, helical domain 1, HD2, helical domain 2; mtDNA, mitochondrial DNA; ROS, reactive oxygen species.