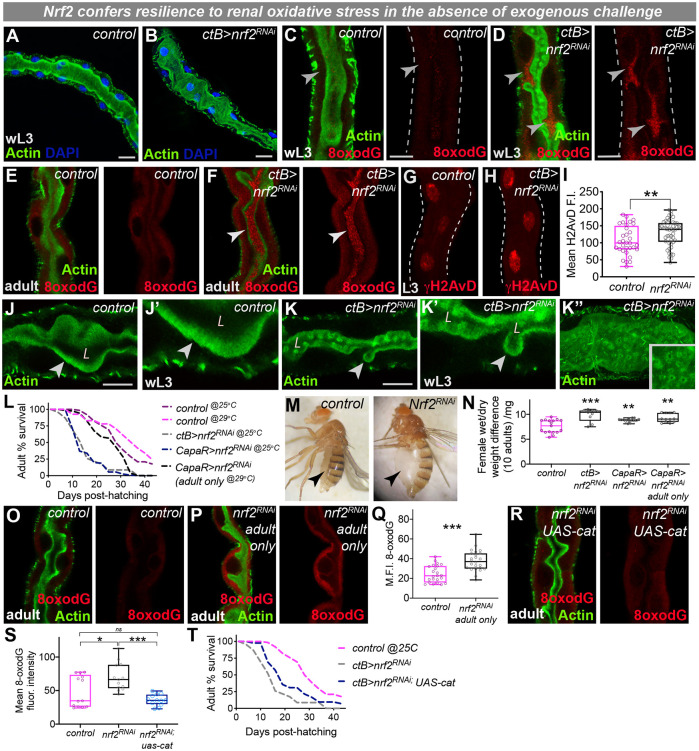
Fig. 5.
Nrf2 confers oxidative stress protection in physiologically active renal tubules. (A-K″) Malpighian tubule (MpT) gross morphology (A,B, L3 tubules; green, Actin; blue, DAPI), oxidative DNA damage (red, 8-oxodG; C,D, L3 tubules; E,F, adult tubules), DNA damage (red, γH2AvD; G-H; quantified in I, L3 tubules) and luminal morphology (green, Actin; J-K, L3 tubules) following ctB-gal4 driven nrf2-RNAi. (L-N) Adult lifespan (L, n>50 per group) and edema (M,N) following nrf2-RNAi-driven inhibition using ctB-gal4 or capaR-gal4. Log-rank comparison of survival curves (L) gave test-statistics of P<0.001 for control25°C versus ctB>nrf2-RNAi, control25°C versus capaR>nrf2-RNAi and control29°C versus capaR>nrf2-RNAi adult only. (O-Q) Oxidative DNA damage (red, 8-oxodG) following nrf2-RNAi in adults only (using capaR-gal4 and tubGal80ts). (R-T) Ectopic catalase expression in ctB>nrf2-RNAi tubules reduced oxidative damage (red, 8-oxodG; R,S) and improved adult survival (T; log-rank test statistic of P=0.018 for ctB>nrf2-RNAi versus ctB>nrf2-RNAi;UAS-cat). Data represented as box and whisker plots (box, 25th to 75th percentile; line, median; whiskers, minimum and maximum values) with all data shown as overlaid points, or line graphs. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 [two-tailed unpaired t-tests (I,Q), one-way ANOVA with multiple comparisons (N,S) or Log-rank survival analyses (L,T)]. All images representative of >7 tubules (A-D,J-K), >10 tubules (E-F,R-T), >30 PCs from >8 tubules (G-I), >100 adults (L) and >15 tubules (O-Q) examined per genotype, condition or developmental stage. M.F.I., mean fluorescent intensity; ns, not significant; wL3, wandering 3rd instar larva. See also Fig. S5. Scale bars: 40 µm (A,D,J,K); 20 µm (G,H,O,U).