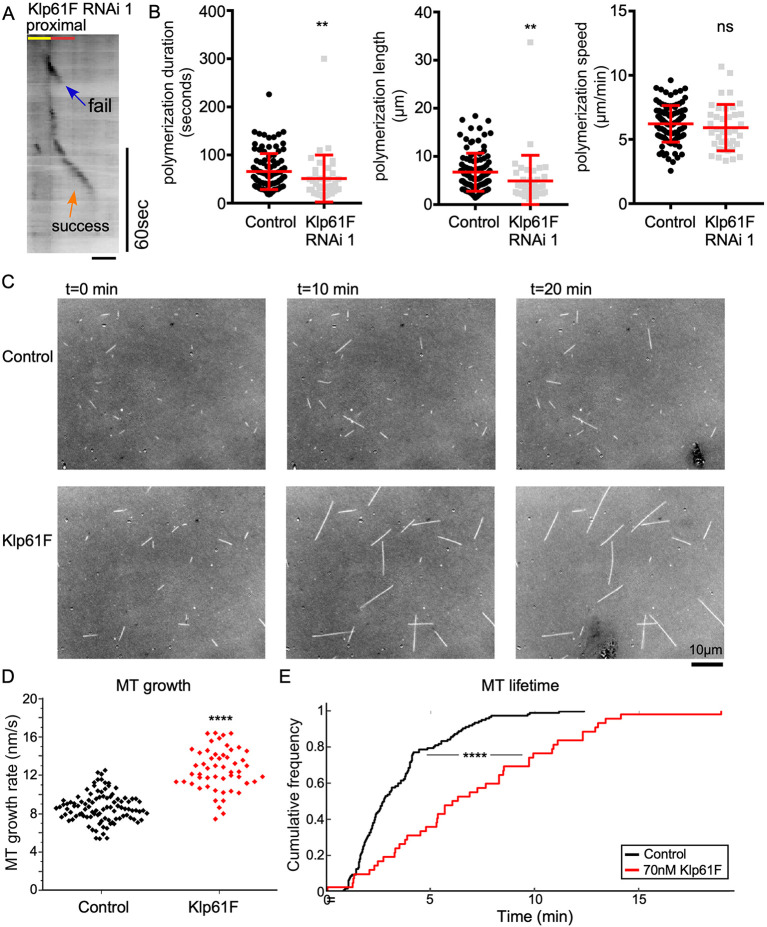
Fig. 6.
Klp61F promotes microtubule polymerization and inhibits catastrophe in vivo and in vitro. (A) Example kymograph of Eb1-GFP at the proximal exit of a ddaE neuron expressing Klp61F RNAi 1. Scale bar: 2 μm. (B) Quantification of microtubule plus-end polymerization under control or Klp61F RNAi conditions. Horizontal lines show the mean, error bars indicate s.d. (C) Snapshots of microtubules generated from seeds incubated with purified tubulin on slides. (D) Quantification of microtubule (MT) polymerization speed of microtubule growth in vitro (nMT=100 for control and nMT=53 for 70 nM Klp61F). An unpaired two-tailed t-test was used to compare the polymerization speeds. (E) Microtubule lifetime was also generated from movies of in vitro polymerization (nMT=123 for Control and nMT=43 for 70 nM Klp61F). **P<0.01; ****P<0.0001; ns, not significant [Kruskal–Wallis test (B); Kolmogorov–Smirnov test was used to compare the two lifetime distributions (E)].