FIGURE 5.
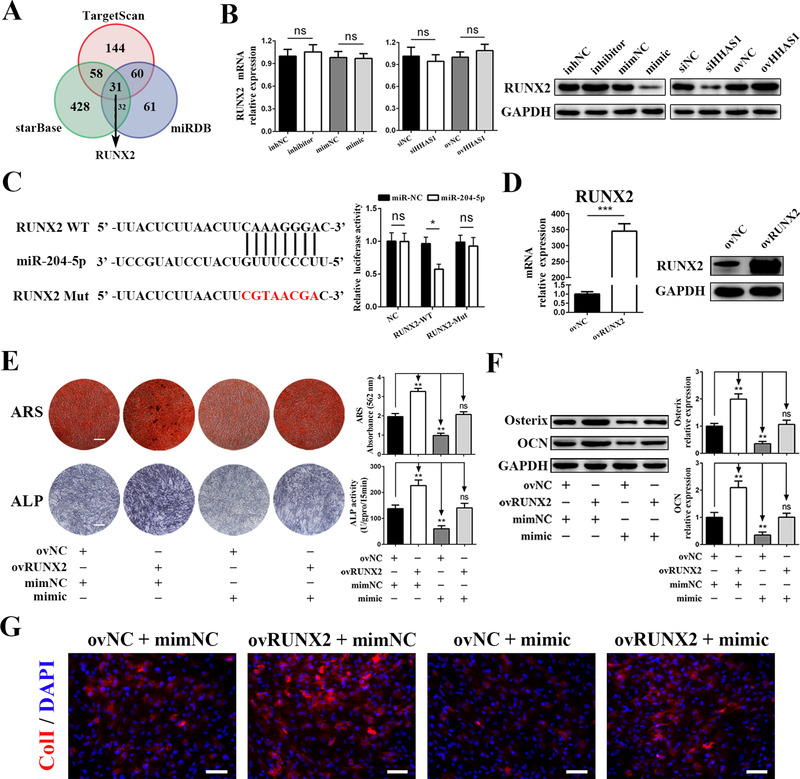
RUNX2 is the target gene of miR‐204‐5p responsible for regulating BMSC osteogenesis. (A) The prediction results of the potential target genes of miR‐205‐5p from TargetScan, starBase, and miRDB database. (B) The miR‐204‐5p mimic, miR‐204‐5p inhibitor, HHAS1 siRNA, and HHAS1‐overexpressing lentivirus did not influence the mRNA levels (left) but changed the protein levels of RUNX2 (right). (C) The binding sites of WT RUNX2 and mutated sites in MUT RUNX2 (left). Dual‐luciferase reporter assays showed that the miR‐204‐5p mimic inhibited the luciferase activity of the RUNX2 WT group but not the RUNX2 MUT group (right). (D) The efficiency of the RUNX2 overexpression was measured by qPCR (left) and western blotting (right). (E) Overexpressing RUNX2 significantly increased the ARS staining, ALP staining and ALP activity of BMSCs and reversed the effect of miR‐204‐5p mimic (scale bar = 200 μm). (F) Overexpressing RUNX2 markedly increased the protein levels of Osterix and OCN in BMSCs and reversed the effect of miR‐204‐5p mimic. (G) Overexpressing RUNX2 significantly increased the fluorescence signal of ColI in BMSCs and reversed the effect of miR‐204‐5p mimic (scale bar = 50 μm). The data are presented as the mean ± SD (n = 10, determined by independent‐sample t‐tests). All experiments were performed three independent times, ns = not statistically significant, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***P < 0.001
