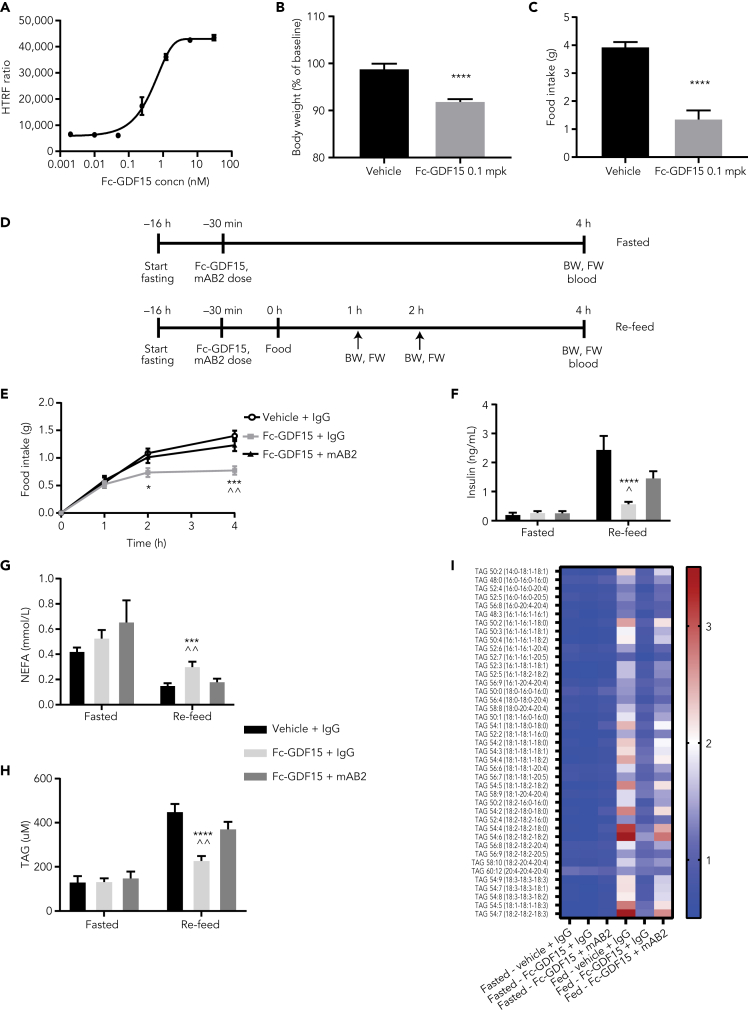
Figure 2.
Validation of mAB2 for acute inhibition of GDF15 in vivo
(A) Activation curve for phospho-ERK using dose response of Fc-GDF15 in GFRAL/RET stable cell line.
(B–C) 24-h body weight (B) and food intake (C) in mice injected with Fc-GDF15 (0.1 mg/kg). ∗∗∗∗ p value < 0.0001 vs. vehicle. Data were analyzed using an unpaired two-tailed t-test.
(D) Schematic representation of the two study designs to test acute inhibition of Fc-hGDF15 by mAB2.
(E) Inhibition of food intake after subcutaneous injection of Fc-GDF15 (0.1 mg/kg) and reversal by cotreatment with mAB2 (10 mg/kg). ∗ p value < 0.004 (2 h), ∗∗∗ p value < 0.0009 (4 h) vs. vehicle + IgG; ˆˆ p value < 0.003 (4 h) vs. Fc-GDF15 + mAB2. Data were analyzed using a longitudinal mixed-effects ANOVA.
(F) Plasma insulin. ∗∗∗∗ p value < 0.0002 vs. vehicle + IgG; ˆ p value < 0.05 vs. Fc-GDF15 + mAB2. (G) NEFA, ∗∗∗ p value < 0.0009 vs. vehicle + IgG; ˆˆ p value < 0.007 vs. Fc-GDF15 + mAB2. (H) Triglycerides, ∗∗∗∗ p value < 0.0001 vs. vehicle + IgG; ˆˆ p value < 0.003 vs. Fc-GDF15 + mAB2, (F–H) Data were analyzed using ANOVA. (I) Heatmap representing fold change in plasma lipid levels when compared with baseline. Data represented as mean ± SEM. N = 10 per group.
ANOVA, analysis of variance; BW, body weight; Concn, concentration; ERK, extracellular signal-regulated kinase; FW, food weight; GDF15, growth differentiation factor 15; GFRAL, glial-cell-derived neurotrophic factor receptor alpha-like; IgG, immunoglobulin G; mpk, mg/kg; NEFA, nonesterified fatty acids; RET, rearranged during transfection; SD, standard deviation; SEM, standard error of the mean; TAG, triglycerides.