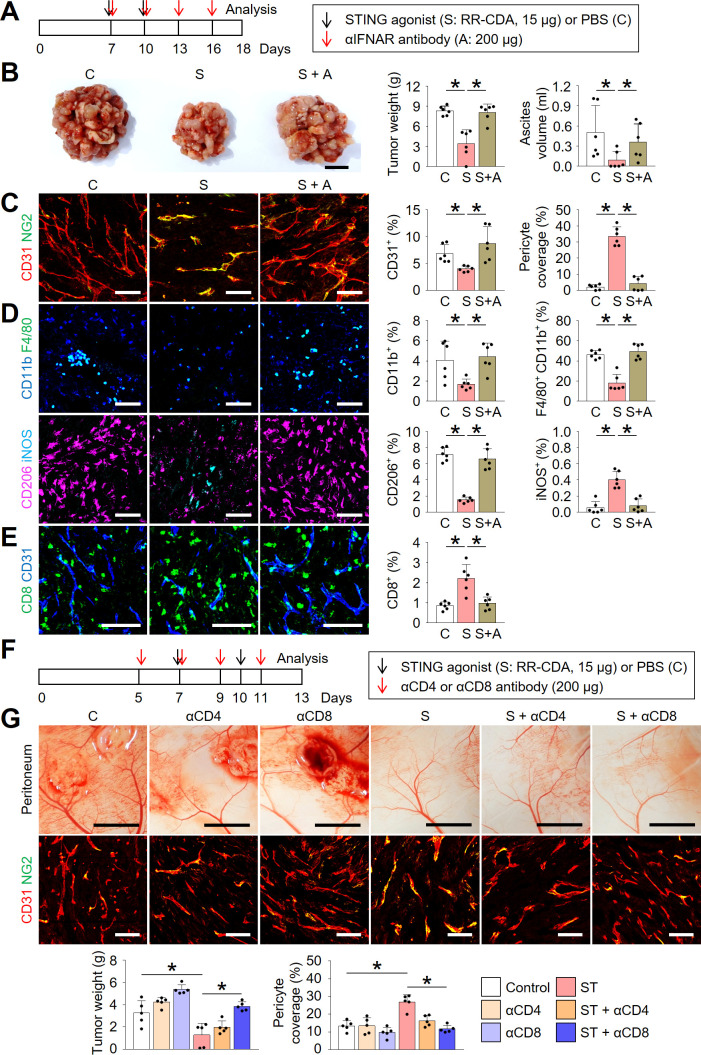
Figure 5.
Type-I IFN signaling and CD8+ T cells are indispensable during STING-induced peritoneal vascular and immune normalization. Mice were injected with MC38 cells intraperitoneally and treated with STING agonist and/or depleting antibodies against IFNAR (αIFNAR), CD4 (αCD4), or CD8 (αCD8). (A) Schematic diagram depicting the treatment schedule for IFNAR depletion study. (B) Representative images and comparison of the peritoneal tumor burden, and comparison of malignant ascites. (C) Representative images and comparisons of CD31+ blood vessels and NG2+ pericyte coverages within tumors. (D) Representative images and comparisons of CD11b+ myeloid cells, CD11b+F4/80+ TAMs, CD206+ M2-like macrophages, and iNOS+ M1-like macrophages within tumors. (E) Representative images and comparison of CD8+ T cells within tumors. (F) Schematic diagram depicting the treatment schedule for CD4 or CD8 depletion study. (G) Representative images and comparison of the peritoneal tumor burden, CD31+ blood vessels and NG2+ pericyte within tumors. Data are pooled from two experiments with n=6 per group (B–E) and n=5 per group (G). Values are shown as the mean±SD p<0.05; ANOVA with Tukey post-hoc test. Scale bar=10 mm (B), 100 µm (C–E), 5 mm (G, top), 100 µm (G, bottom). ANOVA, analysis of variance; IFN, interferon; IFNAR, IFN α receptor; PBS, phosphate-buffered saline; STING, stimulator of interferon genes.