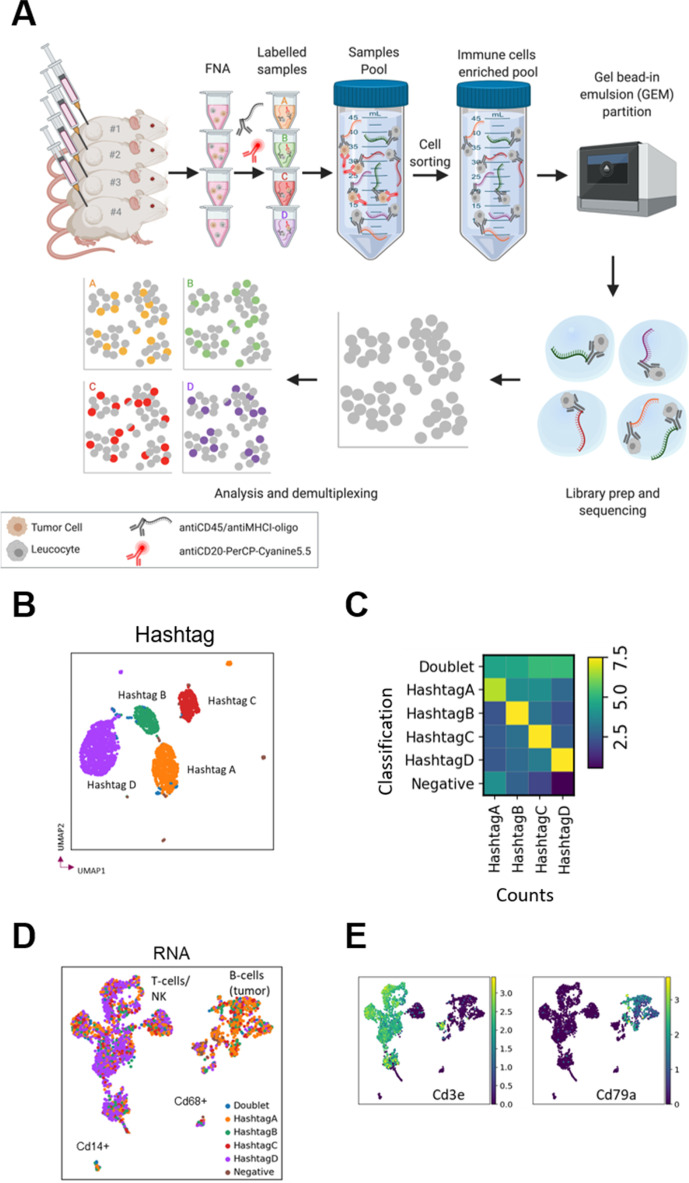
Figure 3.
Fine needle aspiration (FNA) enables single-cell RNA sequencing by multiplexing analysis using cell hashing. (A) FNA biopsies from four mice were labeled with DNA-barcoded antibody ‘hashtags’, pooled, sorted by FACS to enrich for immune cells and sequenced before demultiplexing and analysis. (B) UMAP embedded on hashtags colored by hashtag classification. (C) QC plot of hashtag classification versus counts of hashtag. Cells classified as HashtagA have higher counts for HashtagA, etc, while doublets present a mixed signal, and negative cells show few counts. (D) UMAP embedded on RNA colored by hashtag classification with putative cell types labeled. (E) Expression of the genes for the T cell marker CD3 and the B cell marker CD79a. UMAP, Uniform Manifold Approximation and Projection.