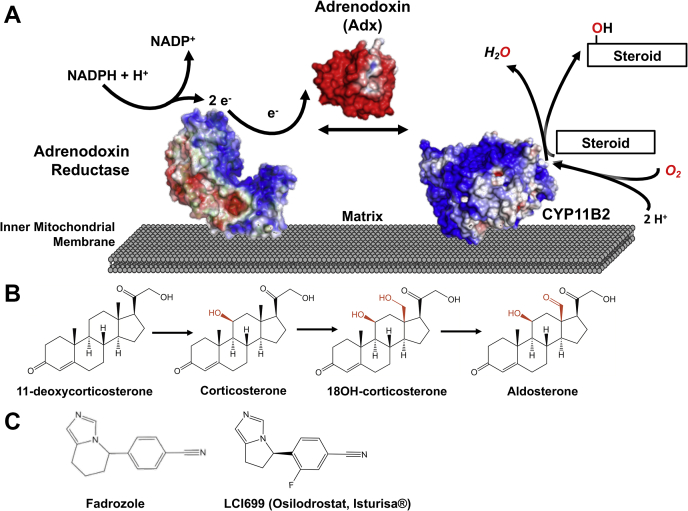
Figure 1.
CYP11B2 catalytic system, reactions, and inhibitors.A, the aldosterone synthase catalytic system is composed of CYP11B2 and FAD-containing adrenodoxin or ferredoxin reductase in the inner mitochondrial membrane plus the soluble iron–sulfur protein adrenodoxin. In the first step NADPH transfers two electrons to the FAD of adrenodoxin reductase. This FAD then transfers one electron at a time to the iron–sulfur cluster of soluble adrenodoxin. Finally, adrenodoxin binds and transfers one electron at a time to CYP11B2 to enable catalysis. B, CYP11B2 converts the substrate 11-deoxycosterone to corticosterone, which is subsequently hydroxylated at position 18 yielding 18OH-corticosterone. A final oxidation at position 18 results in aldosterone. Each of the three reactions requires two electrons, for a total of six electrons. C, the inhibitor fadrozole was initially developed as breast cancer drug and is produced as racemate containing the R and S enantiomer. The (R)-fadrozole derivative LCI699 was initially designed as aldosterone synthase inhibitor, but the selectivity was opposite that desired and this compound is now the first US Food and Drug Administration–approved drug for CYP11B1 inhibition to treat Cushing’s disease.