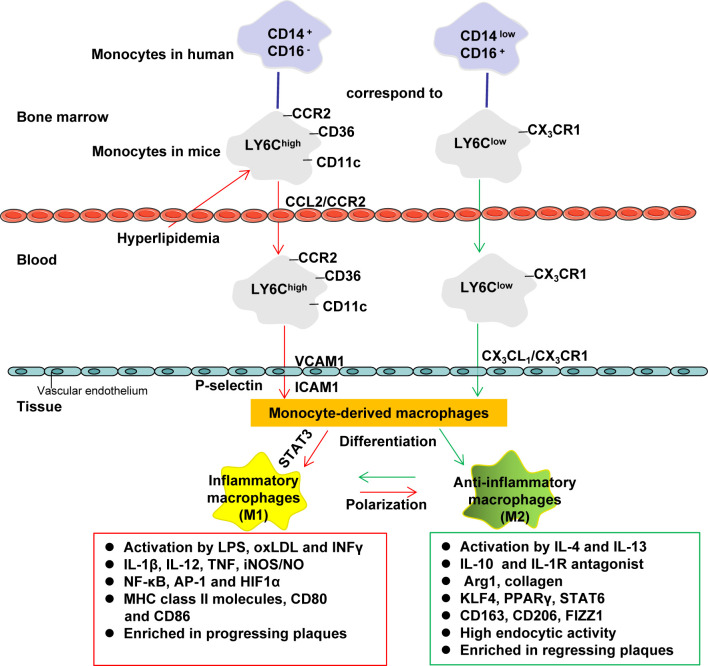
Figure 2.
Monocyte differentiation and macrophage polarization. Monocytes are derived from the hematopoietic precursors of bone marrow or spleen and produce the classic lymphocyte antigen 6C (LY6C) high in mice (corresponding to human CD14high CD16low monocytes), and nonclassical-LY6Clow in mice (corresponding to human CD14low CD16high monocytes). LY6Chigh monocytes highly express CCR2, which can be recruited by chemokines (such as CCL2) to inflammatory sites (including atherosclerotic plaques) to play a pro-inflammatory effect (it is considered to be the precursor of M1 macrophages). Hypercholesterolemia promotes the production of LY6Chigh monocytes by inducing the proliferation of bone marrow precursors. LY6Clow monocytes (considered to be the precursor of M2 macrophages) highly express CX3CR1. These monocyte subpopulations use different chemokine-chemokine receptor pairs to penetrate into the inner membrane, and then differentiate into macrophages in the inner membrane (LY6Chigh is more likely to differentiate into M1 macrophages, while LY6Clow is more likely to differentiate M2 macrophages). M1 macrophages amplify the inflammatory effect by secreting pro-inflammatory cytokines. M2 macrophages help tissue repair by secreting anti-inflammatory cytokines and collagen. AP-1, activator protein 1; Arg1, arginase 1; CCL, C−C motif chemokine; CCR, C-C chemokine receptor; CD, cluster of differentiation; FIZZ1, found in inflammatory zone 1; HIF1α, hypoxia-inducible factor 1α; ICAM1, intercellular adhesion molecule-1; INFγ, interferon-γ; iNOS, inducible nitric oxide synthase; IL, Interleukin; IL-1R, Interleukin 1 receptor; KLF4, Krüppel-like factor 4; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; NO, nitric oxide; NF-κB, nuclear factor kappa B; PPAR, peroxisome proliferator activated receptor; STAT, Signal transducer and activator of transcription; VCAM1, vascular cell adhesion protein 1.