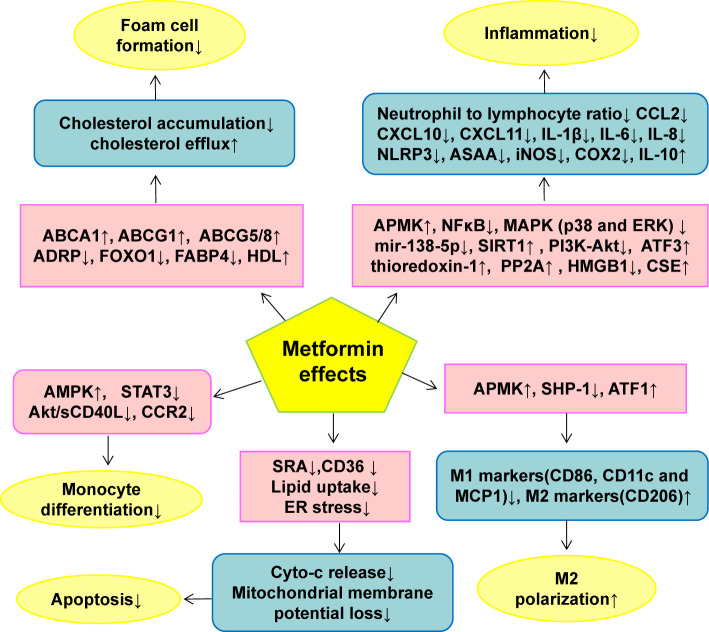
Figure 3.
The effect of metformin on monocyte/macrophage functions in AS. Metformin inhibits monocyte/macrophage dysfunction via modulating the expression and activity of genes or proteins closely related to monocyte differentiation, macrophage inflammation, M1/M2 polarization, foam cell formation and macrophage apoptosis. ↑indicates increase or activation, and ↓indicates decrease or suppression. ABCA1, ATP-binding cassette transporter A1; ABCG1, ATP-binding cassette transporter G1; ABCG5/8, ATP-binding cassette transporter 5/8; ADRP, adipogenic differentiation-associated protein; Akt, protein kinase B; AMPK, 5’-adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase; ASAA, acute-phase serum amyloid A; ATF, Activation of transcription factor; CCL2, C-C motif chemokine ligand 2; CCR2, CC chemokine receptor 2; CD, cluster of differentiation; CXCL, Chemokine C-X-C ligand; CSE, Cystathionine γ-lyase; cyto-c, cytochrome c; ER, endoplasmic reticulum; ERK, Extracellular signal-regulated kinase; FABP4, Fatty acid binding protein 4; FOXO1, Forkhead box transcription factor O1; HDL, high-density lipoprotein; HMGB1, high mobility group box-1; iNOS, inducible nitric oxide synthase; IL, Interleukin; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; MCP1, Monocyte chemoattractant protein 1; NF-κB, nuclear factor kappa B; NLRP3, NOD-like receptor family pyrin domain containing 3; PI3K, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; PP2A, protein phosphatase 2A; sCD40L soluble CD40 ligand; SH2, Src homology 2; domain-containing protein tyrosine phosphatase 1(SHP-1), SIRT1, Sirtuin-1; SRA, scavenger receptor class A; STAT3, Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3.