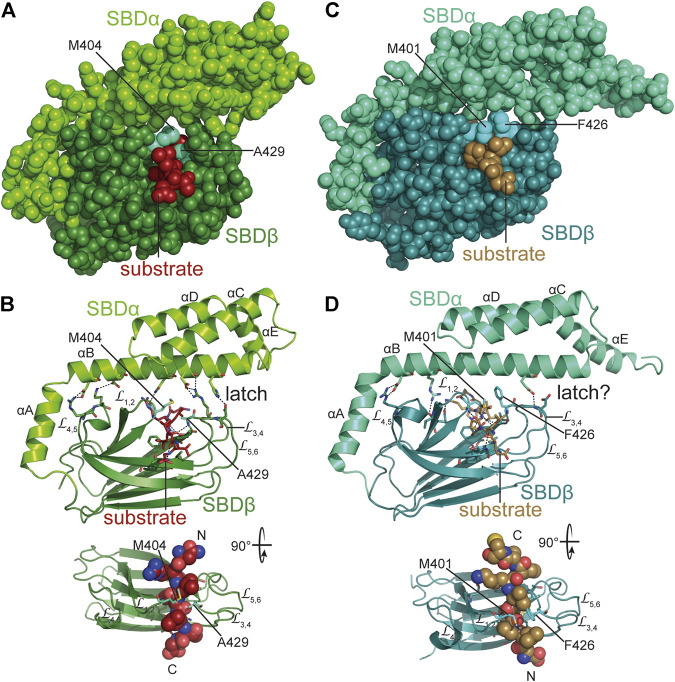
FIGURE 6.
Interaction of Hsp70s with peptide substrates. (A,B), crystal structure of E. coli DnaK SBD in complex with a peptide substrate (NRLLLTG) in space-filling representation (A) and as cartoon (B) [1DKX, (Zhu et al., 1996)]. Polar contacts between SBDβ and SBDα, as well as, between SBDβ and substrate peptide are shown as black dashed lines. Arch forming residues M404 and A429 are labeled. Lower panel, SBDβ rotated as indicated with substrate peptide in space-filling representation and N-and C-terminus of the bound peptide labeled with N and C. (C,D), crystal structure of the SBD of E. coli HscA in complex with a peptide (ELPPVKIHC) comprising the interaction sequence in IscU [1U00, (Cupp-Vickery et al., 2004)] in space-filling (C) and cartoon (D) representation. Arch forming residues M401 and F426 are labeled. Whether the single hydrogen bond between SBDα and outer loops of SBDβ functions as a latch is unclear. Lower panel, SBDβ rotated as indicated with substrate peptide in space-filling representation and N-and C-terminus of the bound peptide labeled with N and C.