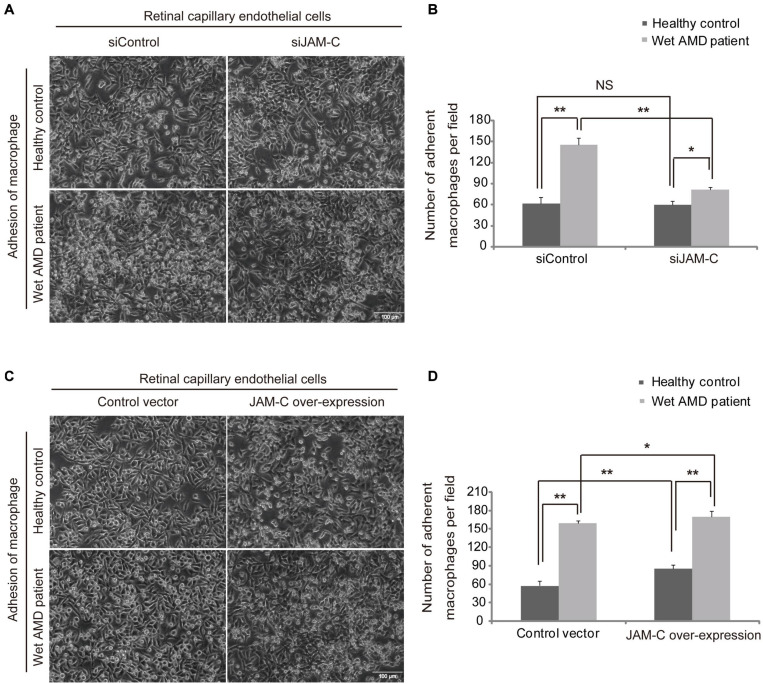
FIGURE 4.
JAM-C regulates macrophage adhesion to human RCECs. Macrophages from wAMD patients or healthy controls were added to culture plate wells containing a confluent monolayer of human RCECs, and the plates were incubated for 1 h. After washing the wells with PBS, adherent cells in five random fields were counted. Adherent macrophages were identified based on the cell size and morphology. (A,B) JAM-C knockdown in RCECs inhibits the adhesion of macrophages (small and round in shape) from wAMD patients to RCECs, but not those from healthy controls. The adhesion ability of macrophages from wAMD patients in both the siControl and siJAM-C groups increased compared to that of macrophages from healthy controls. (C,D) JAM-C overexpression increased the adhesion of macrophages from both wAMD patients and healthy controls. The adhesion ability of macrophages from wAMD patients in both the control and JAM-C overexpression groups increased compared to those from healthy controls. Scale bar: 100 μm, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, NS, not significant.