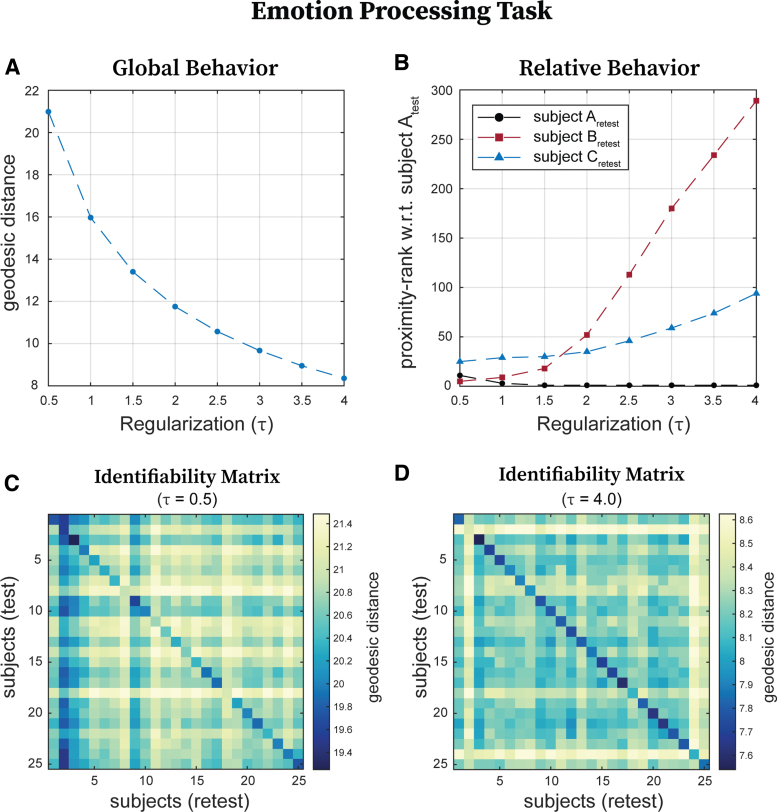
FIG. 2.
Effect of regularization (τ) on global and relative geodesic distances. We have chosen the emotion processing FCs to illustrate how geodesic distances across subjects and/or sessions change with regularization magnitude. (A) Global geodesic distance (in this case averaged geodesic distance between test and retest sessions of all subjects for the emotion processing task) decreases exponentially with increasing regularization. (B) Shows how close (in terms of proximity-rank with respect to all the other subjects) retest sessions of subjects A, B, and C are to the test session of subject A. Note that the three proximity-ranks fluctuate with regularization. (C) Identifiability matrix based on geodesic distance for low () regularization for a subsample of 25 subjects performing the emotion processing task. (D) Identifiability matrix based on geodesic distance for high () regularization for the same subsample of 25 subjects performing the emotion processing task. Color images are available online.