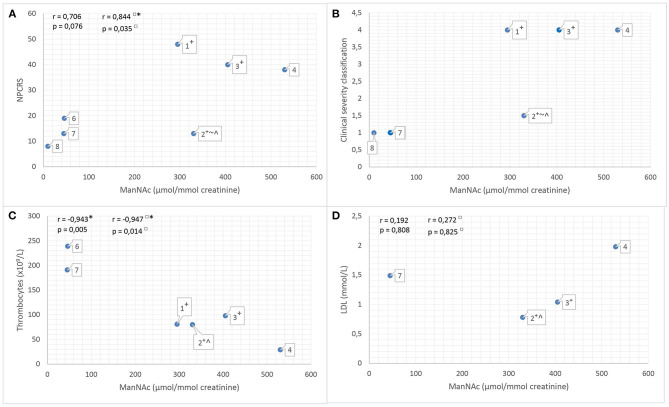
Figure 6.
(A) ManNAc excretion levels in urine (μmol/mmol creatinine, measured by 1H NMR spectroscopy, reference value not detected) vs. the Nijmegen Pediatric CDG Rating Scale (NPCRS) for currently reported patients in whom a ManNAc excretion level was determined. (B) ManNAc excretion levels in urine (μmol/mmol creatinine, measured by 1H NMR spectroscopy, reference value not detected) vs. the clinical severity classification for currently reported patients in whom a ManNAc excretion level was determined. (C) ManNAc excretion levels in urine (μmol/mmol creatinine, measured by 1H NMR spectroscopy, reference value not detected) vs. thrombocyte count for currently reported patients in whom a ManNAc excretion level and thrombocyte counts were measured. If the thrombocyte counts were measured several times, we used the lowest value. (D) ManNAc excretion levels in urine (μmol/mmol creatinine, measured by 1H NMR spectroscopy, reference value not detected) vs. LDL level for currently reported patients in whom a MaNAc excretion level and LDL were measured. If the LDL level was measured several times, we used the lowest value. (A–D) Label numbers indicate the patients. □, analyses excluding patient 2; *, significant at the 0.05 level; †, patients harbor the same mutation [c.709C>T p.(Arg237Cys); c.562T>C p.(Tyr188His)]; ~, in patient 2 (aged 3 months) the NPCRS score and clinical severity classification were low compared to his ManNAc excretion level. Important developmental milestones are not relevant at this young age, explaining why the clinical severity classification is lower than expected on the basis of ManNAc excretion level; ∧, patient is treated with prenatal and postnatal experimental sialic acid; CDG, congenital disorder of glycosylation; ManNAc, N-acetylmannosamine; 1H NMR, quantitative proton nuclear magnetic resonance; NPCRS, Nijmegen Pediatric CDG Rating Scale; r, Pearson linear correlation coefficient.