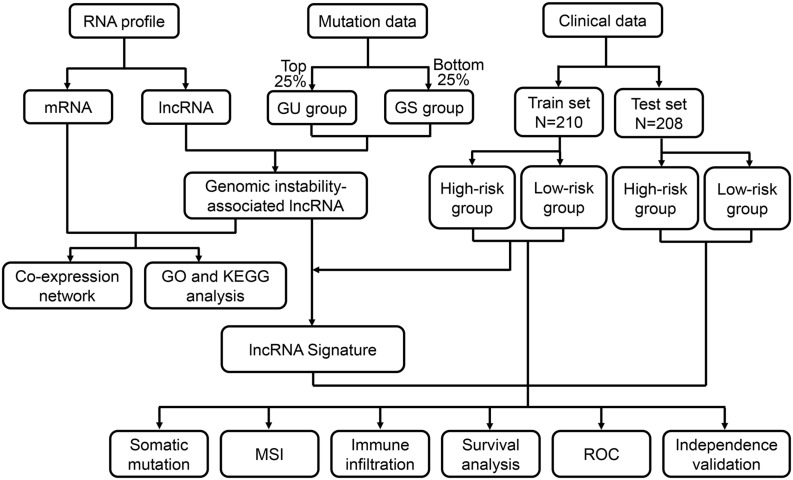
FIGURE 1.
Flow chart of the procedure applied in this study. The RNA profiles, mutation counts and clinical characteristics of colon cancer patients were downloaded from the TCGA database. Genome instability-associated lncRNAs were obtained after the identification of the differentially expressed lncRNAs between the two groups of patients with the top 25% and bottom 25% mutation count frequencies. After identifying the correlated mRNAs, a mRNA-lncRNA co-expression network was constructed, and functional enrichment analysis was performed. After combining the lncRNA data and the overall survival data, a lncRNA signature was developed for clinical outcome prediction. According to the calculated risk score, patients in the training set and testing set were classified into high- and low-risk groups. Correlation of risk score, somatic mutation, microsatellite instability (MSI) and immune infiltration was analyzed. The prognostic prediction efficiency was verified through survival analysis, receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves and independent validation. GU, genome unstable; GS, genome stable; TCGA, The Cancer Genome Atlas; GO, Gene Ontology; KEGG, Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes.