Fig. 1.
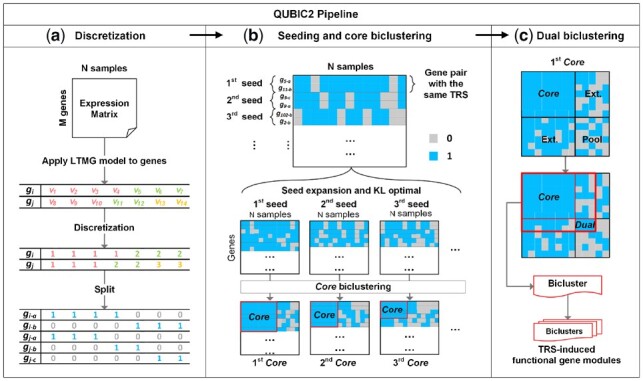
Illustration of QUBIC2 algorithm design. (a) Discretization of gene expression data. The LTMG model was applied to fit the expression profile of a gene. A representing row for each gene was generated with integers denoting the most likely component distribution that an expression value belongs to, and then this representing row was split into multiple rows. Finally, a binary representing matrix was generated after applying the above procedure to all the genes; (b) Core biclustering. By sorting all the gene pairs (seeds) in decreasing order of their weight, an initial seed list was obtained. For a feasible seed, QUBIC2 selected highly correlated genes with the seed in support of the build of an initial Core. (c) Dual biclustering. QUBIC2 expanded the Core vertically and horizontally to recruit more genes and conditions under a preset consistency level, respectively. The intersected zone created by extended genes and conditions formed a searching pool. QUBIC2 identified a Core in the pool (denoted as Dual) using the same procedure in b and output the bicluster with genes and conditions that came from the Core and Dual
