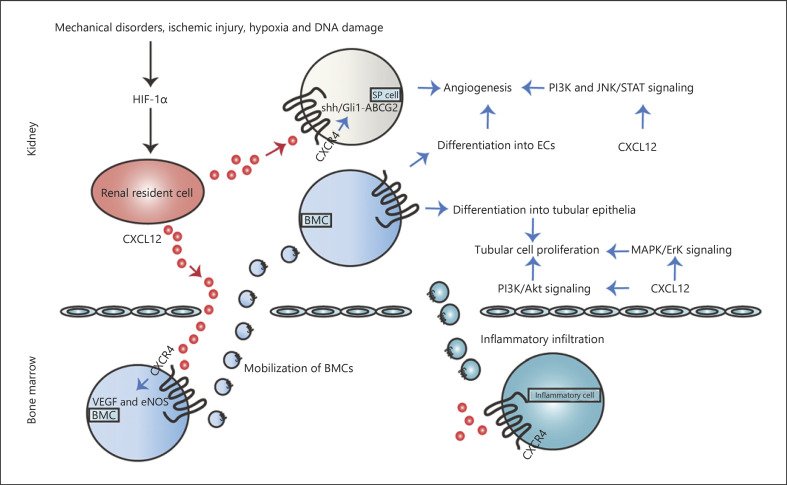
Fig. 1.
Correlation between CXCL12 and AKI. Various pathological stimuli induce HIF-1α, which enhances the CXCL12/CXCR4 axis, ultimately improving AKI regeneration. On the one hand, the CXCL12/CXCR4 axis promotes angiogenesis by VEGF and eNOS-mediated BMCs differentiation into ECs, SP cells-initiated recovery via Shh/Gli 1-ABCG2 pathway. In addition, diverse signaling pathways are also involved, such as PI3K and JNK/STAT signaling pathways. Additionally, the CXCL12/CXCR4 axis also increases tubular cell proliferation due to BMCs differentiation into the tubular epithelia and diverse pathways activation, such as PI3K/Akt and MAPK/Erk signaling pathways. Furthermore, CXCL12-induced inflammatory infiltration including neutrophils infiltration, T-cell depletion, and macrophage initiation is also involved in AKI. AKI, acute kidney injury; EC, endothelial cell; BMC, bone marrow-derived cell; eNOS, endothelial nitric oxide synthase; SP, side population; TEC, tubular epithelia cell.